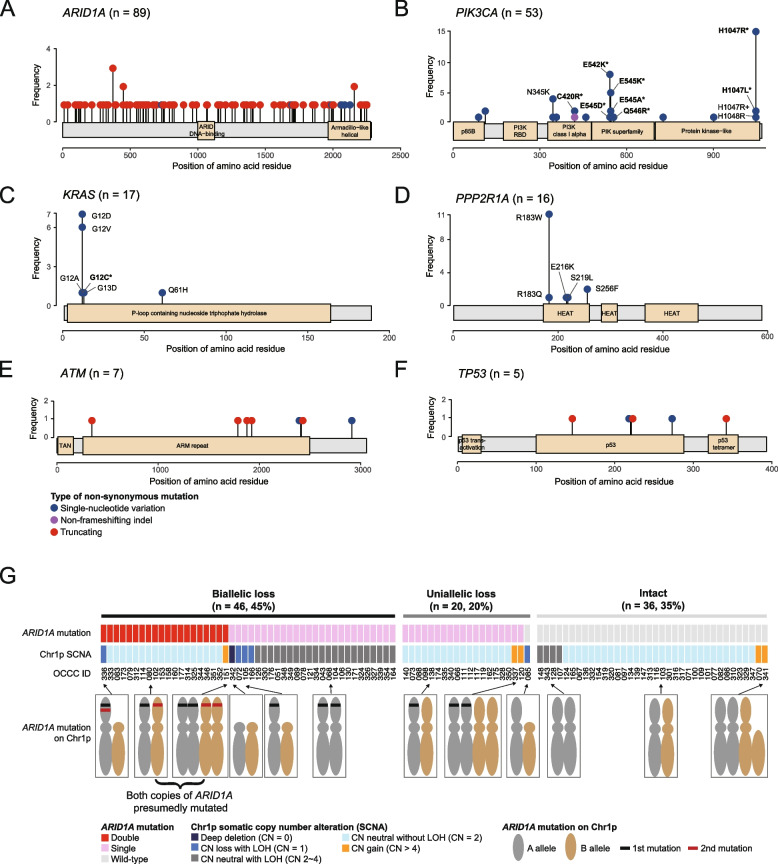
Fig. 3.
Types and frequencies of mutations in six driver genes: (A) ARID1A, (B) PIK3CA, (C) KRAS, (D) PPP2R1A, (E) ATM, and (F) TP53 gene. Selected mutation types were annotated accordingly. Mutations that fall within the tier 1 or 2 clinical actionability are emphasized using asterisk (*) markings. G Loss of tumor suppressor genes in the OCCC tumors. Biallelic loss is defined as having either of the following conditions: 1) double truncating mutations with or without loss-of-heterozygosity (LOH), 2) single truncating mutation with LOH, or 3) complete copy number loss (copy number of zero). Uniallelic loss is defined as having either of the following conditions: 1) single truncating mutation without LOH, 2) Copy number loss without truncating mutation