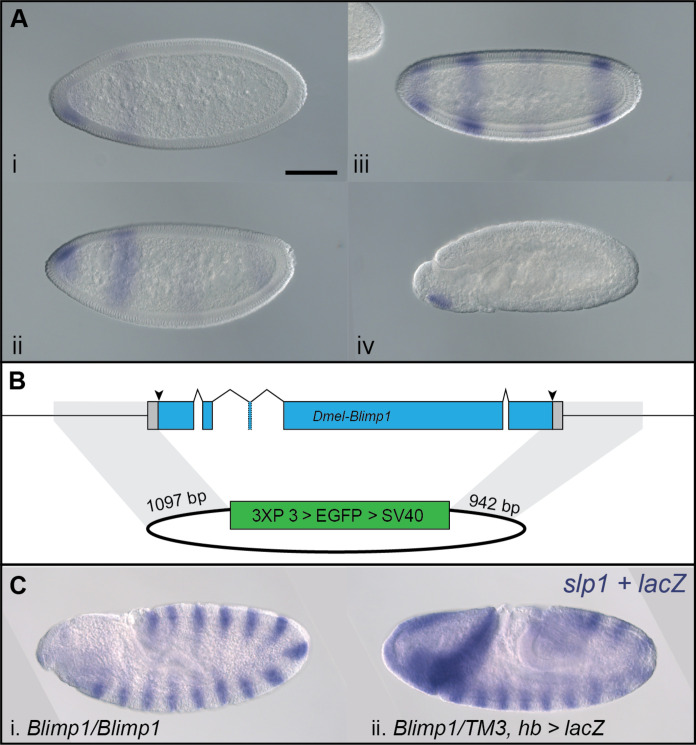
Fig. 7. Dm-Blimp1 is not required to establish segments in Drosophila.
(A) Dm-Blimp1 is expressed in early Drosophila embryos. Expression begins in the head followed by formation of a single anterior (i) and additional of two weak posterior stripes (ii). Most Dm-Blimp1 expression then intensified, but the central stripe appeared as two weak stripes (iii). After germ-band formation, Dm-Blimp1 expression was detected only in the head region (iv). (B) Null Dm-Blimp1 allele generated with CRISPR-Cas9. Schematic showing the Dm-Blimp1 gene, which includes five exons. gRNA target sites (arrowheads) were designed to remove the entire coding region. The homology-directed repair plasmid template included ~1-kb homology arms on either side of a 3XP3 > EGFP expression cassette for creation of the Dm-Blimp13XP3 > EGFP allele, in which the entire Dm-Blimp1 CDS is replaced by the 3XP3 > EGFP dominant marker. Homology arms are highlighted in gray. (C) Blimp13XP3 > EGFP homozygous mutants do not show segmentation defects. Blimp13XP3 > EGFP homozygotes and (i) Dm-Blimp13XP3 > EGFP heterozygotes (ii) displayed indistinguishable, wild-type expression of Dm-slp, a segmental marker. Note that heterozygotes also express lacZ in an hb-like pattern due to a transgene on the balancer chromosome. Scale bar, (A, i) 100 μm.