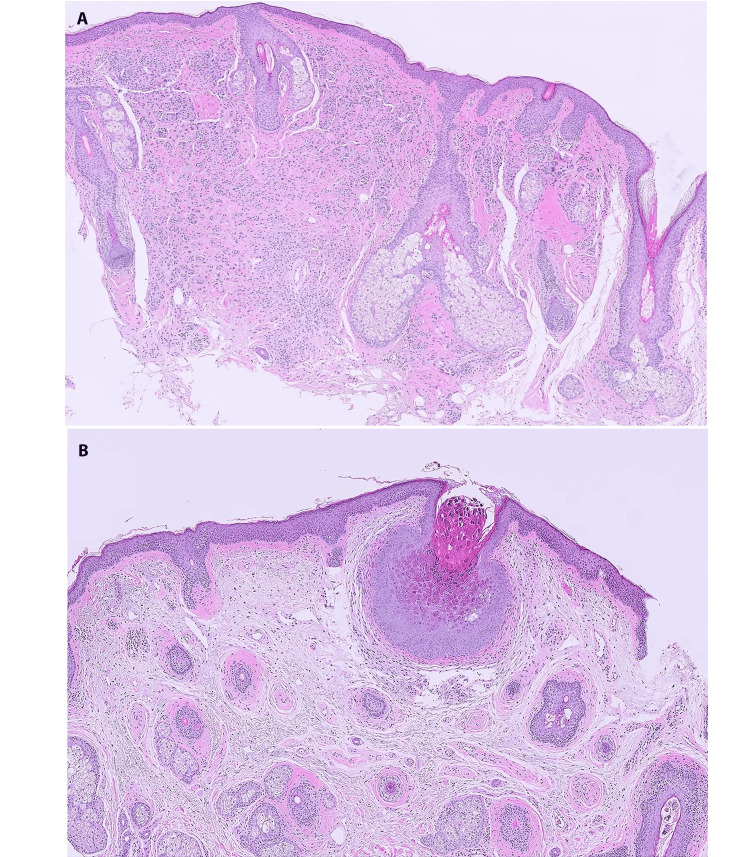
Figure 2. Molluscum contagiosum in an intradermal nevus.
(A) Intradermal nevus, high power view, showing the characteristic dermal melanocytic proliferation. (B) Normal squamous epithelium flanking a cup-shaped lesion with an inverted lobule of hyperplastic squamous epithelium expanding into the superficial dermis. The epithelial cells show nuclei compressed by eosinophilic intra-cytoplasmic viral inclusions, molluscum bodies, seen at higher magnification. Note the disappearance of most dermal nevus cells in the areas adjacent to the molluscum (H&E, x50).