Fig. 5 |. Proposed model of organization within the nucleus.
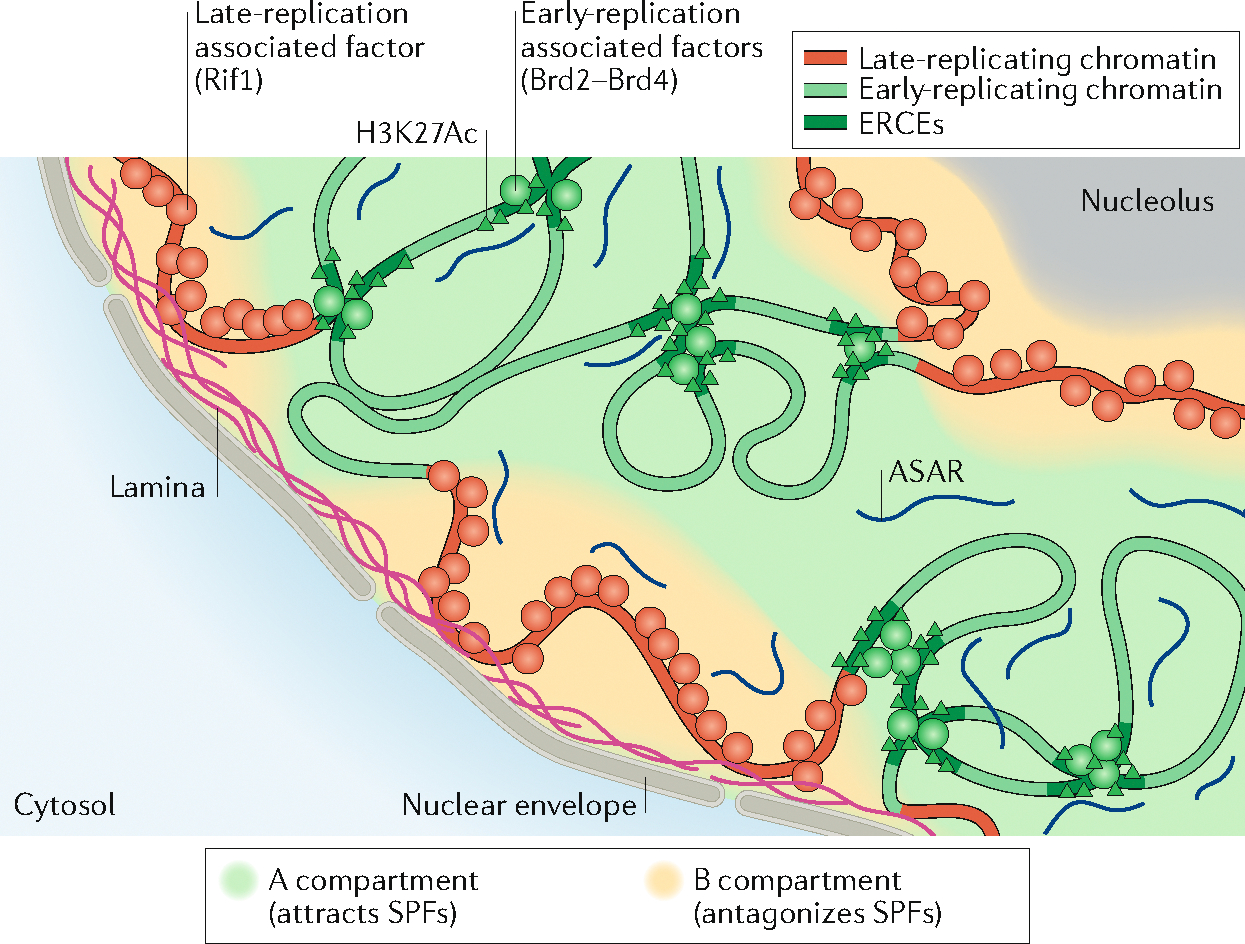
Model for the compartmentalization of the nucleus into and early- and late-replicating chromatin regions. In this model, early-replicating regions, within the A compartment, contain elements rich in H3K27Ac, bound by factors such as Brd2 and Brd4 that recruit S-phase-promoting factors (SPFs; see FIG. 4) such as Treslin. These elements, called early-replication control elements (ERCEs), form a platform for recruiting SPFs within the domain in which they belong. In this model, the replication of late-replicating regions, within the B compartment and associated with the nuclear lamina and the nucleolus, would be delayed by factors inhibiting origin firing (that is, antagonizing SPFs), such as Rif1 (which antagonizes DDK). At the chromosome level, coating of each chromosome by long non-coding RNAs known as asynchronous replication and autosomal RNAs (ASARs) could ensure the presence of replication machinery factors within each chromosome territory.
