FIGURE 6.
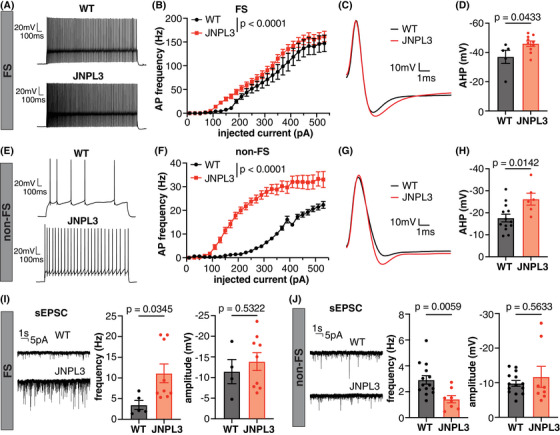
Increased excitability and altered excitatory synaptic transmission in L2/3 motor cortical neurons in JNPL3 mice. (A) Representative AP firing pattern in an FS neuron from a WT or JNPL3 mouse. Neurons were injected with a 290 pA depolarization current for 1 s. (B) F/I curve of FS neurons in WT or JNPL3 brain slices. Slight but significant left shift of F/I curve in JNPL3 FS neurons compared to WT controls. (C) Representative AP waveforms fired by FS neurons with minimal current injection. (D) AHP potential significantly increased in JNPL3 FS neurons, compared to WT controls. (E) Exemplar traces of AP firing pattern in non‐FS neurons injected with a 290 pA depolarization current for 1 s. (F) F/I curve of non‐FS neurons in WT or JNPL3 brain slices. Significant left‐shift of F/I curve in JNPL3 non‐FS neurons, compared to WT controls. (G) Representative AP waveforms fired by non‐FS neurons with minimal current injection. (H) AHP potential significantly increased in JNPL3 non‐FS neurons. (I) Frequency and amplitude of sEPSC in FS neurons. A significant increase of sEPSC frequency but not amplitude was observed in JNPL3 FS neurons. (J) Frequency and amplitude of sEPSC in non‐FS neurons. A significant decrease of sEPSC frequency but not amplitude was observed in JNPL3 non‐FS neurons. Two‐way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test in (B) and (F). Unpaired t‐tests in (D), (H), (I), and (J). AHP, After‐hyperpolarization; AP, action potential; F/I, frequency current; FS, fast‐spiking; non‐FS, non‐fast‐spiking; sEPSC, spontaneous excitatory post‐synaptic current; WT, wild‐type.
