FIGURE 2.
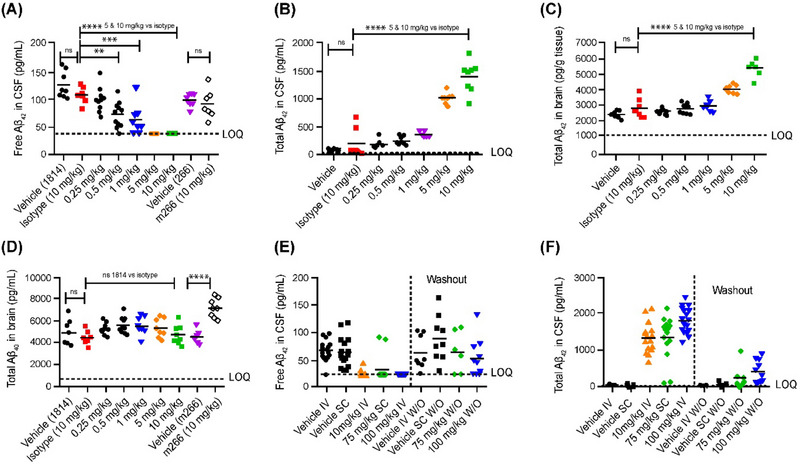
Pharmacodynamics of MEDI1814 in Sprague–Dawley rats. Intravenous administration of MEDI1814 and m266 twice over 14 days with samples collected 7 days post second dose (A–D). Maximal suppression of free Aβ42 was observed at 5 and 10 mg/kg, with significant effects being observed at 0.5–10 mg/kg relative to isotype control. Dose‐dependent increase of total (bound and free) Aβ42 is observed both CSF and brain. Total Aβ40 in the brain was unaffected by either isotype control or MEDI1814, showing selectivity of MEDI1814 for Aβ42 in the brain. MEDI1814 dosed 14 times over 13 weeks, with samples collected 8 weeks after the final dose (E and F). Free Aβ42 in CSF decreased in all the MEDI1814 treatment groups after 14 weekly doses (E). Total CSF Aβ42 increased dose‐dependently in the 10 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg IV and 75 mg/kg SC groups compared to the appropriate vehicle group after 14 doses (F). At the end of the treatment‐free period, 8‐ and 3.5‐fold higher total Aβ42 levels in the CSF were observed in the 100 mg/kg IV and 75 mg/kg SC groups, respectively. Concentrations shown are absolute in pg/mL as determined by ELISA. One‐way analysis of variance and Tukey multiple comparison: ns p ≥ 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. Aβ, amyloid beta; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous.
