FIGURE 3.
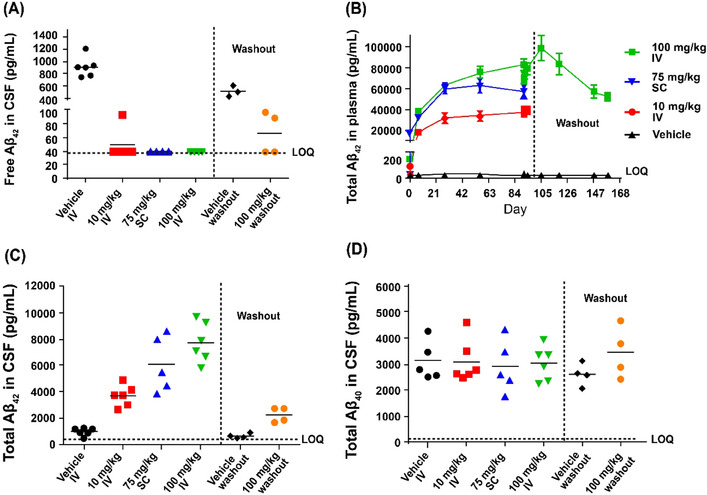
Pharmacodynamics of MEDI1814 in cynomolgus monkeys. Intravenous weekly administration of MEDI1814 over 13 weeks in cynomolgus monkey: (A), free CSF Aβ42; (B) total plasma Aβ42; (C) total CSF Aβ42; (D) total CSF Aβ40. A dose‐dependent increase in total Aβ42 in both plasma and CSF was observed at the end of the treatment phase in the 10 mg/kg IV, 100 mg/kg IV, and 75 mg/kg SC groups. The majority of free Aβ42 (> 95%) was suppressed in CSF at all dose levels at the end of the treatment phase (A). At the end of a 9‐week treatment‐free period, total Aβ42 levels in plasma increased in the 100 mg/kg IV dose group compared to the vehicle group (B); compared to the vehicle group, total CSF Aβ42 was higher, though not significant (C), and free CSF Aβ42 was suppressed. The specificity of MEDI1814 binding to Aβ42 over Aβ40 was confirmed by lack of effect on total CSF Aβ40 at all tested doses (D). Washout denotes a period of 9 weeks after dosing had stopped. Aβ, amyloid beta; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; IV, intravenous; LOQ, limit of quantification; SC, subcutaneous.
