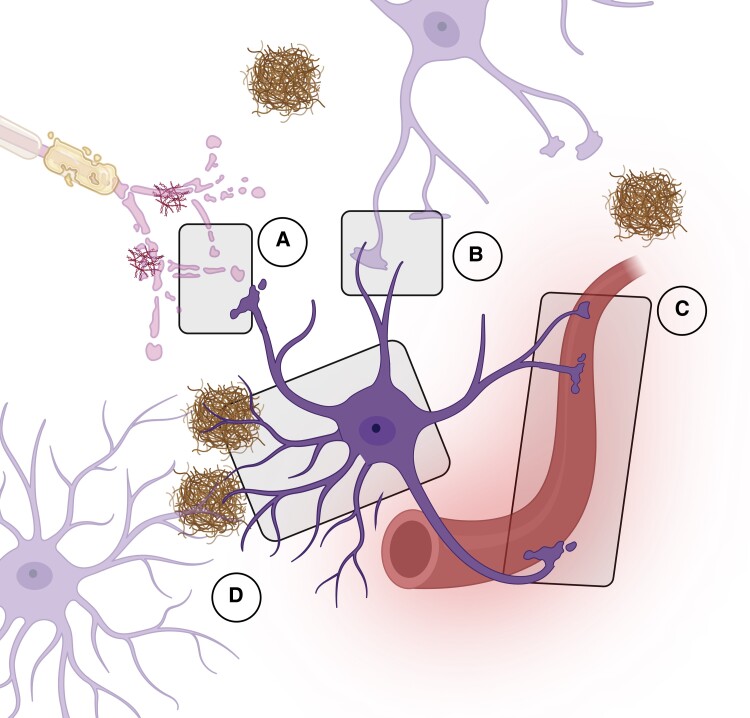
Figure 4.
Astrocytes roles and modifications in Alzheimer’s disease. Due to their multifaced functions and implications in various brain structures, reactive astrocyte modifications deeply impact brain physiology at several levels. (A) Tripartie synapses: Alteration of neurotransmitter and glutamate pathways, modification of water and ion channel transport and release of inflammatory substances leading to synaptic disfunctions, neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation; (B) Astrocytes tight junction: Irregular ion transient (Ca2+, K+) and decreased gap junctions coupling; (C) Astrocytes endfeet surrounding the blood–brain barrier (BBB): Release of overexpressed GFAP due to astrocytes impairment associated with BBB disruption and immune-cell massive infiltration; (D) Astrocytes morphology: Astrocytes structural atrophy and proliferation confining amyloid lesions and inducing Aβ clearance through the glymphatic pathway. Neurofibrillary tangles internalization.