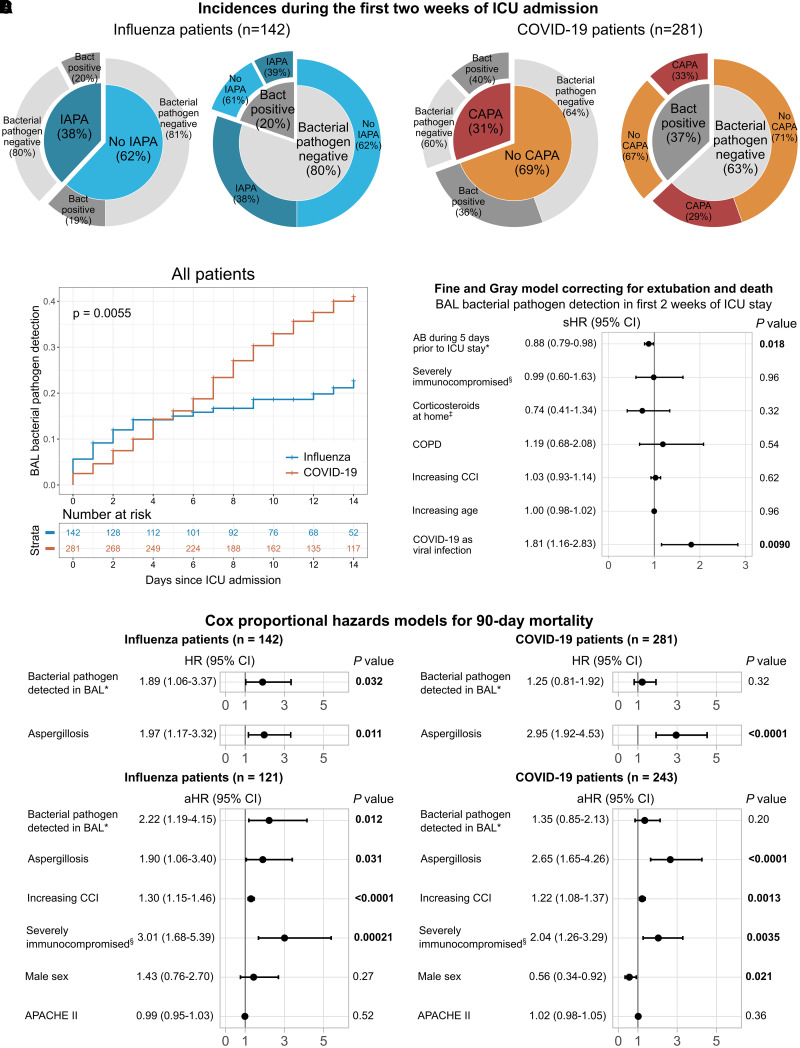
Figure 1.
Incidence and associations with outcome of a positive culture or PCR for a bacterial pathogen in BAL fluid, or invasive aspergillosis, during the first 2 weeks of ICU admission in patients mechanically ventilated for influenza or coronavirus disease (COVID-19). (A) Incidence of invasive aspergillosis and bacterial pathogen identification in BAL fluid in the first 2 weeks since ICU admission, subdivided in the influenza and COVID-19 cohorts. (B) Cumulative incidence curves of patients with influenza and patients with COVID-19 showing incidence of a positive bacterial pathogen in BAL culture or PCR during the first 2 weeks of their ICU stay. Censoring was performed at extubation, death, or after 14 days after ICU admission. Gray’s test P value is shown. Risk table shows the number of patients at risk at the start of the day since ICU admission. (C) Forest plot showing the results of the Fine and Gray model for 14-day incidence of a positive bacterial pathogen BAL culture or PCR, correcting for competing risks (extubation or death) and relevant clinical factors. Fine and Gray model incorporating antibiotic and corticosteroids use during ICU stay can be found in Figure E2. *Number of days on antibiotics during the 5 days preceding ICU stay. §Severely immunocompromised, as defined by the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and Mycosis Study Group Education and Research Consortium (EORTC/MSGERC) host factors for invasive mold disease (34). ‡Low-dose (below EORTC/MSGERC cutoff) corticosteroids as home medication. (D) Cox proportional hazard models for 90-day mortality in patients with influenza or COVID-19. Two univariable models (with bacterial pathogen identification in BAL fluid during the first 2 weeks of ICU admission, or aspergillosis throughout the ICU stay) and a similar model with additional relevant clinical variables are shown for the influenza cohort and the COVID-19 cohort. The number of patients included in the large multivariable models is lower because of missing data for APACHE II scores on ICU admission. In all models, bacterial pathogen identification and aspergillosis are modeled as time-dependent variables. *Detected in BAL fluid during the first 2 weeks of ICU stay through culture or PCR. §Severely immunocompromised, as defined by the EORTC/MSGERC host factors for invasive mold disease (34). Cox proportional hazards models for 30-day mortality are illustrated in Figure E3. AB = antibiotics; APACHE II = Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; Bact = bacterial; CAPA = COVID-19–associated pulmonary aspergillosis; CCI = Charlson Comorbidity Index; CI = confidence interval; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HR = hazard ratio; IAPA = influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis; sHR = subdistribution hazard ratio.