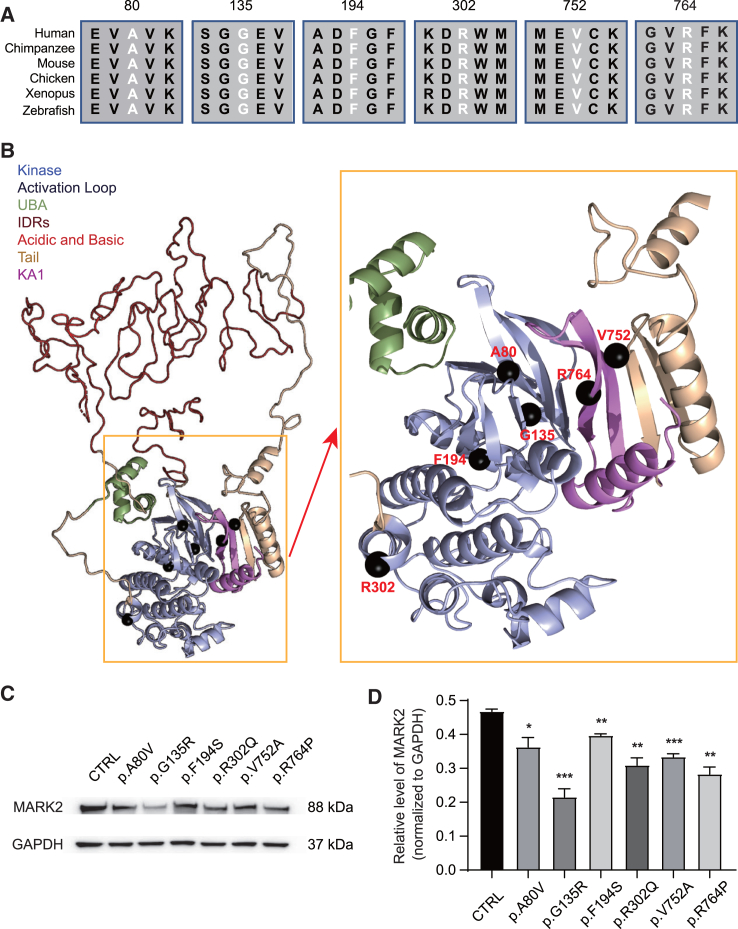
Figure 2.
Structural modeling of six MARK2 missense variants
(A) Alignment of the protein sequences for 6 MARK2 missense variants across species from zebrafish to humans.
(B) 3D structural models of MARK2 missense variants. The protein domains of MARK2 are shown in different colors. The 3D structures of the non-intrinsically disordered regions (non-IDRs) were used to compute the changes in structural stability due to genomic variation. Amino acids in the IDRs are shown in a disordered configuration; we expect that any individual configuration of the IDRs would be an inadequate representation of their diverse dynamics. The locations of the 6 missense variants are marked by black spheres. Four variants in the kinase domain (p.A80V, p.G135R, p.F194S, p.R302Q) and 2 variants in the KA1 domain (p.V752A, p.R764P) were all predicted to locate in the activation loop.
(C and D) Representative western blot image (C) and quantification analysis of exogenous MARK2 accumulation that were normalized by total GAPDH levels (D). Human HEK 293T cells transfected with wild-type (CTRL) or mutant EGFP-MARK2-Neo vectors were lysed. The data of at least 3 independent experiments were analyzed by Student’s t test ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.