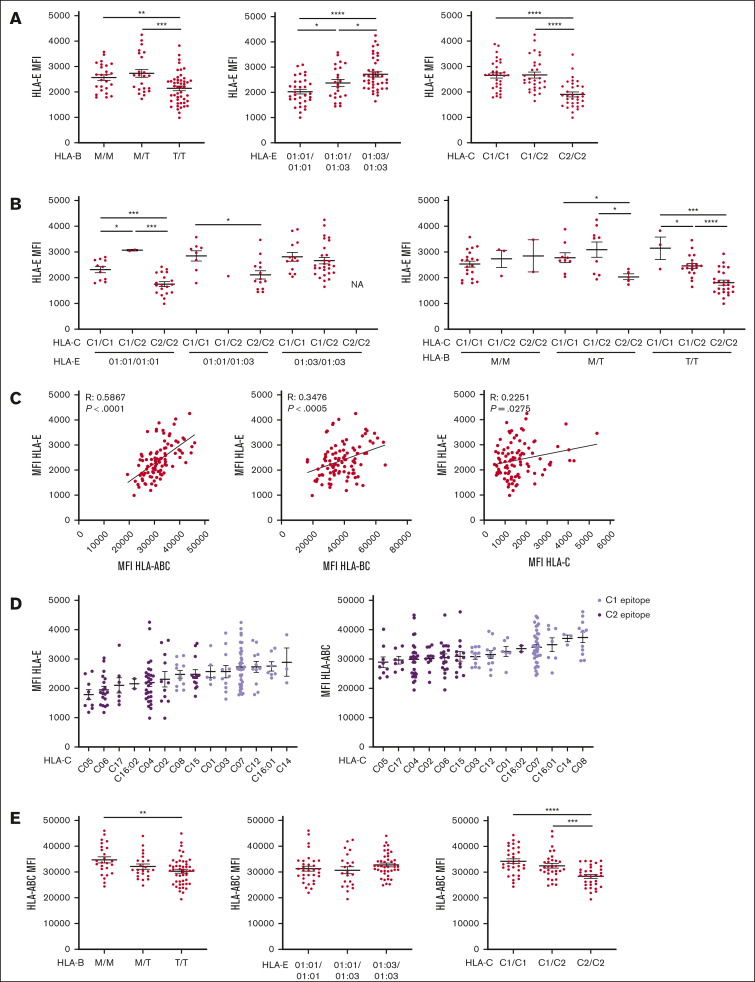
Figure 4.
HLA-E expression depends on the quantity of HLA class I signal peptide available and associates with HLA-C epitopes. All HLA MFI were measured on CD3+ CD56– T cells. (A) HLA-E MFI segregated by HLA-B leader peptide, HLA-E allele, or HLA-C epitope. (B) HLA-E MFI is segregated by HLA-E and HLA-C epitopes or by HLA-B leader peptide and HLA-C epitopes. (C) Correlation between HLA-E MFI and HLA class I expression, as measured by anti-HLA-ABC, anti-HLA-BC, and anti-HLA-C. (D) HLA-ABC and -E MFI grouped by HLA-C alleles, color-coded by HLA-C KIR ligand epitope, and ranked in ascending order. (E) HLA-ABC MFI segregated by HLA-B leader peptide, HLA-E allele, and HLA-C epitope. For panels A-B,E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panel C. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.