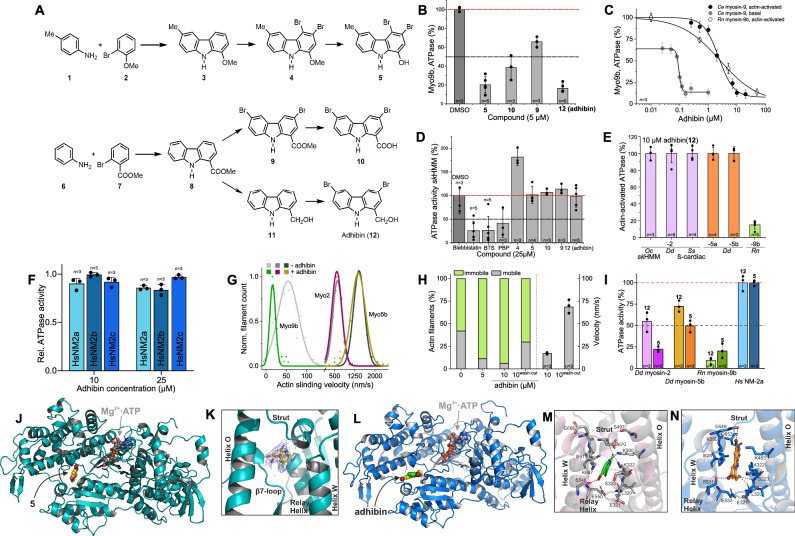
Fig. 1. Identification of adhibin as a myosin class-IX specific inhibitor.
A Chemical structures and synthetic routes of compounds (details provided in ‘Materials and Methods’). B Efficacy of compounds to inhibit Rnmyosin-9b actin-activated ATPase activity. C Inhibitory effect of adhibin on Cemyosin-9 and Rnmyosin-9b basal and actin-activated ATPase activities. D Effect of compounds on basal ATPase activity of skeletal myosin-2 (skHMM) in comparison to blebbistatin, BTS, and PBP. E Effect of adhibin (12) on actin-activated ATPase of myosins from class-II, -V and -IX. F Inhibitory effect of adhibin on actin-activated ATPase activity of NM2A, 2B, and 2C. G Effect of adhibin on the motile activity of Cemyosin-9, Ddmyosin-2 and Ddmyosin-5b. H Motile vs immotile actin filaments after incubation with adhibin. Recovery of motile properties after wash-out of adhibin. Data derived from measurements of 80–200 filaments. I Inhibition of actin-activated ATPase activity of different myosins by 5 and 12 at 25 µM concentrations. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. J Crystal structure of Ddmyosin-2 motor domain in complex with ADP-VO3 and adhibin analogue 5. K The 2Fo − Fc density map of 5, contoured at 1.0 σ. 5 binds to a pocket surrounded by the strut, β7-loop, relay helix, O-helix and W-helix. L Homology model of Myo9a from rat showing the adhibin binding site. M Close-up view of the adhibin binding pocket in Myo9a and (N) in the homology model of rat Myo9b. Hydrogen (grey dashed lines), halogen bonds (purple dashed lines). n is the number of experiments. All data are represented as mean ± S.D.