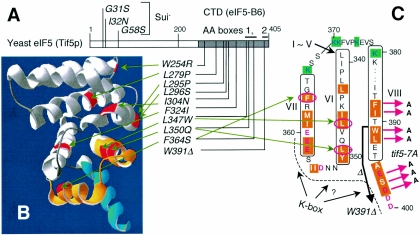
FIG. 1.
The positions of eIF5 point mutations used in this study. (A) Positions of Sui− and Ts− mutation sites are located in the primary structure of yeast eIF5. Numbers indicate eIF5 amino acid positions. The gray region indicates the CTD. Bars above the box denote AA-boxes 1 and 2. (B) The positions of eIF2Bɛ residues homologous to yeast eIF5-CTD mutation sites in panel A are highlighted in red on the solved structure of eIF2Bɛ-CTD (7). AA-box 1 and 2 amino acids are highlighted in orange and blue, respectively. The three-dimensional structure was drawn with DeepView/Swiss-Pdf Viewer (v. 3.7) (Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics). (C) Yeast eIF5 amino acids from positions 339 to 400 are arranged to show secondary structures predicted from Boesen's eIF2Bɛ-CTD structure (7). Essentially, the entire eIF5-CTD is predicted to form eight α-helices, designated helix I (most N-terminal) to helix VIII (most C-terminal). Residues predicted to participate in α-helices VI through VIII are boxed with the helix numbers in Roman numerals. Highlighted with orange are AA-box amino acids (AA-box 1 in helices VI and VII; AA-box 2 in helix VIII), while highlighted with green in blue letters are lysine residues highly conserved in all eIF5s. Conserved acidic residues are shown in red. The dotted line and question mark indicate a possible K box interface. Red arrows indicate tif5-7A mutation sites. The thick arrow indicates the region deleted by tif5-W391Δ. Circled in red are the residues altered by indicated mutations.