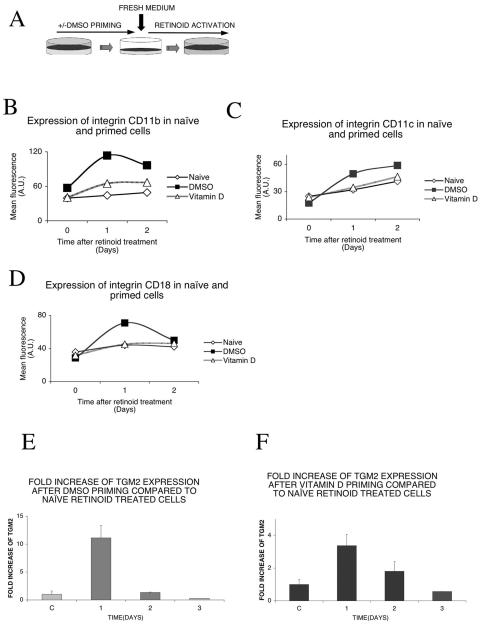
FIG. 1.
Priming enhances retinoid response in HL-60 cells. (A) Experiment outline. HL-60/CDM-1 cells were primed with 1.25% DMSO overnight. The control (naive) cells received no priming. After overnight incubation, cells were washed, resuspended in fresh medium, and treated with 1 μM 9-cis retinoic acid. (B) Priming with DMSO or vitamin D enhances 9-cis retinoic acid-dependent expression of integrin CD11b. Cells were primed with 1.25% DMSO or 100 nM vitamin D. After overnight incubation and washing out of the priming agent, cells were treated with 1 μM 9-cis retinoic acid and analyzed on a flow cytometer at the indicated time points as described in Materials and Methods. Isotype controls had no change (not shown). (C) Priming with DMSO or, to a lesser extent, with vitamin D enhances 9-cis retinoic acid-dependent expression of integrin CD11c. Cells were primed with 1.25% DMSO or 100 nM vitamin D. After overnight incubation and washing out of the priming agent, cells were treated with 1 μM 9-cis retinoic acid and analyzed with a flow cytometer at the indicated time points as described in Materials and Methods. Isotype controls had no change (not shown). (D) Priming with DMSO but not with vitamin D enhances 9-cis retinoic acid-dependent expression of integrin CD18. Cells were primed with 1.25% DMSO or 100 nM vitamin D. After overnight incubation and washing out of the priming agent, cells were treated with 1 μM 9-cis retinoic acid and analyzed with a flow cytometer at the indicated time points as described in Materials and Methods. Isotype controls had no change (not shown). (E) Relative increase of TGM2 mRNA induction compared to that of naive, retinoid-treated cells. Assessment of the maintenance in time of the priming effect: TGM2 mRNA was measured by real-time QPCR after priming with 1.25% DMSO and compared to naive, retinoid-treated cells. After overnight incubation and washing out of the priming agent, cells were treated with 1 μM 9-cis retinoic acid at different time points after the priming, as indicated. The retinoid treatment was 12 h long in all cases. Values are the means of the results from three independent QPCR measurements ± standard deviations. (F) Relative increase of TGM2 induction compared to that of naive, retinoid-treated cells. Assessment of the maintenance in time of the priming effect: TGM2 mRNA was measured by real-time QPCR after priming with 100 nM vitamin D and compared to naive, retinoid-treated cells. After overnight incubation and washing out of the priming agent, cells were treated with 1 μM 9-cis retinoic acid at different time points after the priming, as indicated. The retinoid treatment was 12 h long in all cases. Values are the means of the results from three independent QPCR measurements ± standard deviations.