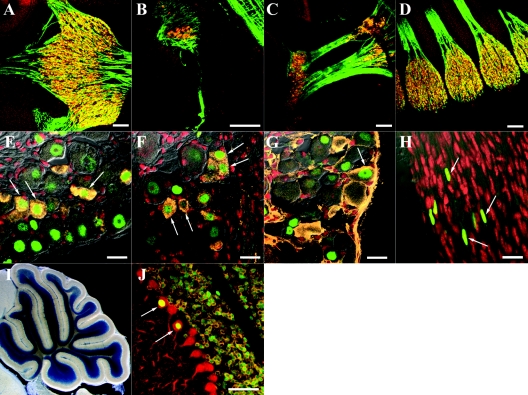
FIG. 5.
Cellular localization of Foxs1 expression. (A to D) Immunostaining of sagittal sections of E11.5 Foxs1β-gal/β-gal embryos with antibodies against β-galactosidase (orange), neurofilament 160 (green), and a nuclear counterstain (red). Foxs1 is expressed in most if not all of the neurons located in the trigeminal (A), vestibulocochlear (B), proximal and distal ganglia of glossopharyngeal and vagal nerves (C), and DRG (D). (E to H) Foxs1 expression in P7 dorsal root ganglia. Immunofluorescence with anti-β-galactosidase antibody (green) and a nuclear counterstain (red) reveals that Foxs1 is not restricted to neurons of a specific sensory modality but colocalizes with several different markers in P7 Foxs1β-gal/β-gal DRG. Colocalization is seen with CGRP (orange) (E), substance P (orange) (F), and parvalbumin (orange) (G). (H) β-Galactosidase-positive cells are also seen along the nerve sheet extending from the DRG. (I and J) Cerebellar expression of Foxs1 in P14 brain. (I) Low-magnification view of X-Gal-stained sagittal section identifying Foxs1 in the internal granule layer. (J) Immunofluorescence analysis with antibodies against β-galactosidase (green), calbindin D28K (red, a marker of Purkinje cells), and GABAA receptor α6 (orange, a marker of granule cells) confirms Foxs1 expression in most or all granule cells as well as in a subpopulation of Purkinje cells (arrows). Bars, 100 μm (A to D), 20 μm (E to H), 50 μm (J).