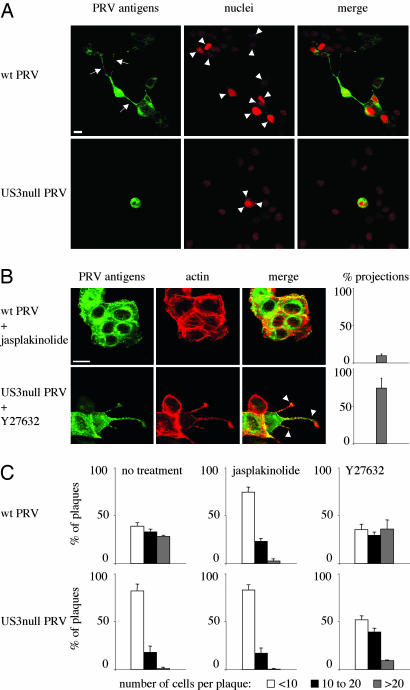
Fig. 5.
The US3-induced cell projections are associated with enhanced virus intercellular spread. (A) Plaques of wild-type (Upper) and US3-null (Lower) PRV in sparsely plated ST cells in the presence of virus-neutralizing antibodies. Cells were methanol-fixed at 24 hpi and stained for viral antigens (green), and nuclei were counterstained by using propidium iodide (red). Arrows indicate projections in cells infected with wild-type virus, arrowheads indicate nuclei that make part of the virus plaques. (Bar, 10 μm.) (B) Addition of 50 nM of the actin-stabilizing drug jasplakinolide to ST cells infected with wild-type PRV (Upper) inhibits formation of projections, whereas addition of 30 μM of the Rho kinase inhibitor Y27632 to cells infected with US3-null PRV induces the formation of cell projections. (Bar, 10 μm.) Graphs on the right indicate the percentage of cell clusters that display projections (compare with Fig. 1 A). Data represent means ± SD of triplicate assays. (C) Effect of addition of 50 nM jasplakinolide or 30 μM Y27632 on plaque size of wild type (Upper) and US3-null (Lower) PRV in sparsely plated ST cells in the presence of virus-neutralizing antibodies. Plaque sizes were measured by determining the number of cells per plaque (white bars, <10; black bars, 10 to 20; gray bars, >20).