FIGURE 2.
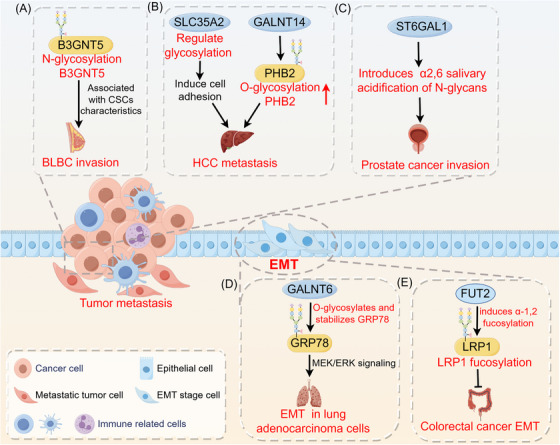
Role of glycosylation in tumor metastasis. Glycosylation has an impact on events related to tumor metastasis, including the stem cell properties of tumor cells, EMT, migration, and invasion. (A) B3GNT5 glycosylation is associated with cancer stem cell properties in basal‐like breast cancer. (B) SLC35A2 promotes HCC metastasis by regulating glycosylations to increase cell adhesion capacity. GALNT14‐mediated PHB2 O‐glycosylation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and migration. (C) ST6GAL1 induces α2,6 salivary acidification of N‐glycans, promoting prostate cancer growth and invasion. (D) GALNT6 interacts with the O‐glycosylated chaperone protein GRP78, enhancing the MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma cells to promote EMT and invasion. (E) FUT2 induces α‐1,2 fucosylation and inhibits colorectal cancer EMT and metastasis via LRP1 fucosylation. Abbreviations: B3GNT5, β1,3‐N‐acetylglucosaminyltransferase 5; BLBC, basal‐like breast cancer; CSCs, cancer stem cells; EMT, epithelial‐mesenchymal transition; FUT2, fucosyltransferase 2; GALNT14, polypeptide N‐acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 14; GALNT6, N‐acetylgalactosaminyltransferase‐6; GRP78, glucose regulatory protein 78; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; LRP1, lipoprotein receptor‐related protein 1; PHB2, prohibitin 2; SLC35A2, solute carrier family 35 member A2.
