FIGURE 4.
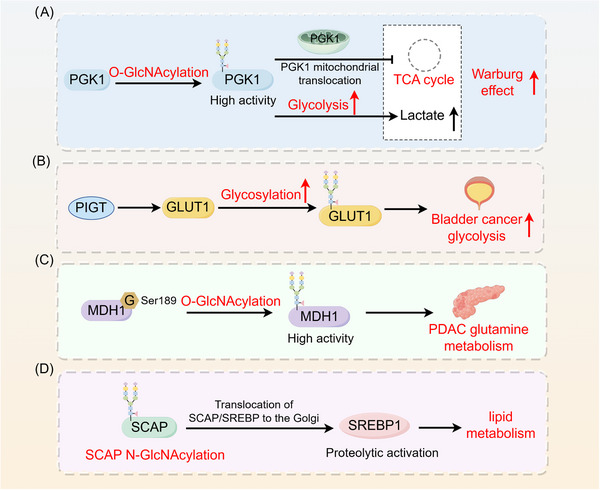
Role of glycosylation in tumor metabolic reprogramming. (A) Glycosylation increases the metabolic enzyme activity of PGK1 and induces PGK1 translocation to mitochondria to inhibit the TCA cycle, thereby enhancing the Warburg effect in cancer cells. (B) PIGT enhances glycolysis in bladder cancer cells through the regulation of GLUT1 glycosylation. (C) O‐GlcNAcylation regulates the metabolic activity of MDH1, promoting glutamine metabolism in pancreatic cancer. (D) SCAP N‐glycosylation promotes SCAP/SREBP translocation to the Golgi apparatus, which in turn activates SREBP1 to regulate lipid metabolism in tumors through SREBP‐dependent lipids. Abbreviations: G, glycosylation; GLUT1, glucose transporter type 1; MDH1, malate dehydrogenase 1; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PIGT, phosphatidylinositol glycan biosynthesis class T; SCAP, SREBP cleavage‐activating protein; SREBP, sterol regulatory element‐binding protein.
