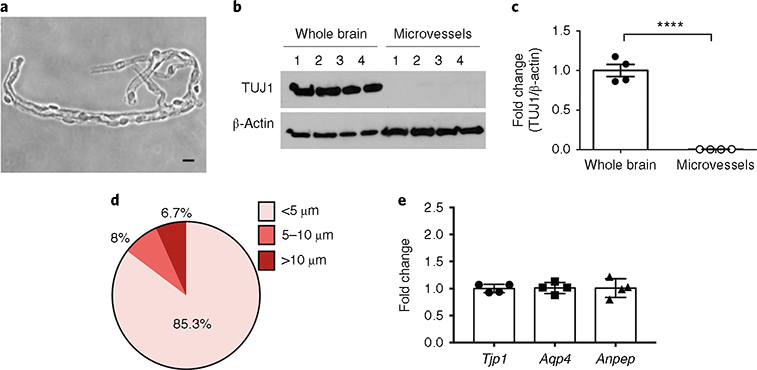
Fig. 2 |. Characterization of microvessel preparations: purity, structural features (size) and consistency in cellular composition.
a, Bright-field (phase-contrast) image of microvessels plated on microscope slides (scale bar, 10 μm). b,c, Purity of the microvessel preparations was assessed by the absence of the neuronal marker TUJ1. Western blot analysis of the neuronal marker TUJ1 in whole-brain and microvessel samples (b) and quantification after normalization with β-actin (c) are shown. ****P < .0001 (t-test). d, The diameters of the microvessel fragments were measured under an inverted microscope (Olympus CKX41) using the built-in tools of the CellSens Entry software. ~1,000 microvessel fragments were measured. e, The cellular compositions of the microvessel preparations were tested. The content of endothelial cells, astrocytes and pericytes in four independent microvessel preparations was assessed by RT-qPCR quantification of Tjp1 (ZO-1, endothelial marker), Aqp4 (astrocyte end-foot marker) and Anpep (CD13, pericyte marker) mRNA levels. Notice the consistent cell composition of the different preparations, as assessed by similar levels of cell-specific markers. RIN is ≥9.8. The individual values and the average ± s.e.m. are shown. Full blots for b are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1.