Figure 7.
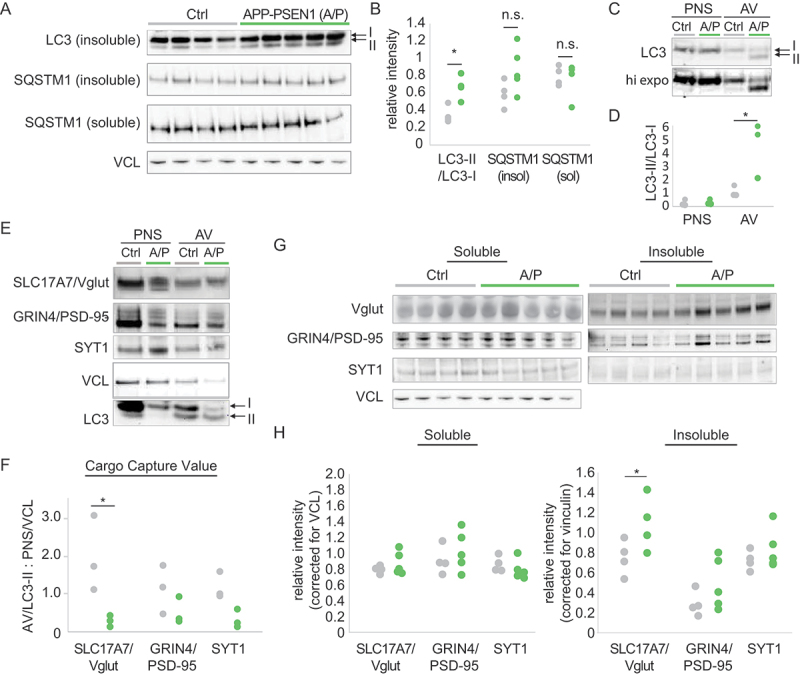
Abnormal autophagic flux in APP PSEN1 mice leads to synaptic protein accumulation. (A and B) Quantitative western blot of Ctrl or APP PSEN1 (A/P) whole forebrain homogenates, fractionated to detergent soluble and insoluble fractions. Blots were probed for MAP1LC3/LC3 or SQSTM1/p62. VCL was used as a loading control. Ctrl, n = 4; A/P, n = 5. Individual data points shown (C-F) Quantitative western blot of AVs isolated from Ctrl or A/P mice and probed for MAP1LC3/LC3. (C) Representative immunoblot for MAP1LC3/LC3. Higher exposure (hi expo) shown to indicate LC3-II levels in the Ctrl AV. (D) LC3-II:LC3-I ratio. (E and F) Quantitative western blot to determine the relative quantity of synaptic proteins cargo such as SLC17A7/Vglut1, DLG4/PSD-95 and SYT1. (F) Cargo capture value (CCV). Represents the relative amount of protein in the AVs, with respect to total protein levels. Protein levels in AVs are normalized to LC3-II, then corrected for the relative amount of the protein in the PNS, normalized to VCL, to account for potential differences in overall protein levels between the two groups. Individual data points for each AV preparation (N) shown. N = 3 AV fractionations/genotype. Each fractionation represents n = 4–5 brains. (G and H) Quantitative western blot of homogenates described in (A), probed for SLC17A7/Vglut1, DLG4/PSD-95, and SYT1. VCL was used as a loading control. Ctrl, n = 4; A/P, n = 5. Individual data points shown. *p < 0.05.
