Figure 3.
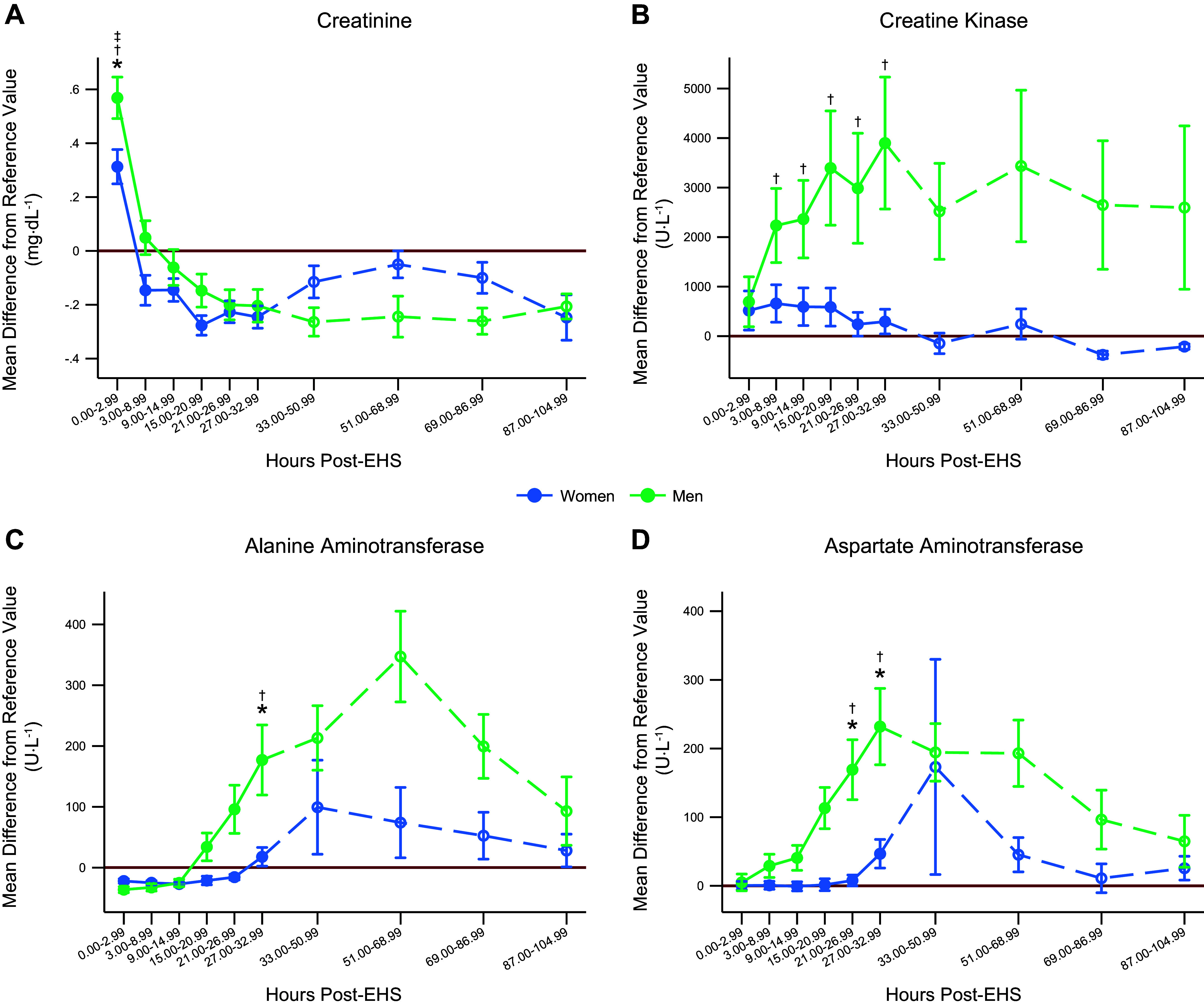
Mean difference (MD) from the upper limit of clinical reference value for men and women. N = 62 EHS, n = 51 men, n = 11 women analyzed using mixed-effects models. Areas of open circles and dashed lines area were not statistically analyzed due to missing data but are shown for clinical relevance. To calculate MD, the measured value for each individual was subtracted from the respective upper limit. An MD of zero means the measured value is equal to the upper limit. Since men and women have different limits, this allows us to assess how far the mean for men and women are from their respective upper limits and compare that difference between the sexes. A: MD data for creatine. B: MD data for creatine kinase. C: MD data for alanine aminotransferase. D: MD data for aspartate aminotransferase. For 33.00–104.99 h post-EHS, labs were combined into 18-h intervals due to a prevalence of missing data. As a result, there was not enough statistical power to assess those time points, but they are presented for clinical relevance and are denoted with a dashed line. N = 62 (51 men, 11 women). *Statistically significant difference between men and women P < 0.05. †Statistically significant difference from the upper limit for men P < 0.05. ‡Statistically significant difference from the upper limit for women P < 0.05. EHS, exertional heat stroke.
