Figure 3.
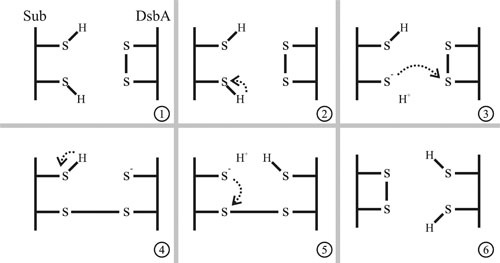
The mechanism of disulfide bond formation. DsbA catalyzes the formation of disulfide bonds in a polypeptide with reduced cysteines. The cysteines within the Cys-X-X-Cys active site of DsbA are oxidized (S-S), and the thiol side-groups of cysteine residues in the substrate are reduced (SH) (panel 1). Disulfide bond formation is initiated by deprotonation of a thiol group in the substrate (panel 2). The resulting thiolate anion can initiate a nucleophilic attack on the disulfide bond of DsbA (panel 3). The resolution of the mixed-disulfide bonded complex could occur by deprotonation of another thiol group (panel 4), which can attack the substrate-DsbA disulfide bond (panel 5). The result of this reaction is the oxidation of the substrate and the reduction of DsbA (panel 6).
