Figure 5.
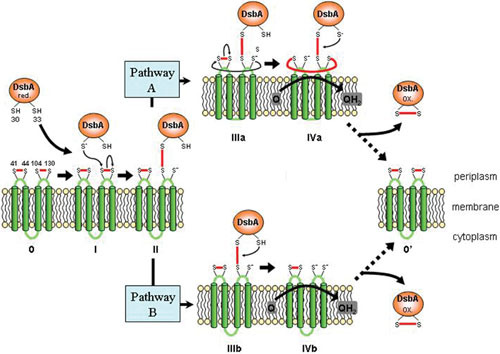
Mechanism of DsbA reoxidation by DsbB. A reduced DsbA interacts with oxidized DsbB, resulting in the reoxidation of DsbA and reduction of DsbB. The DsbA-DsbB complex is formed via a disulfide bond between C33 of DsbA and C104 of the second periplasmic loop of DsbB. The resolution of this complex is believed to occur through two pathways. In pathway A, a disulfide bond is formed between the first and second periplasmic loop, which is resolved by the oxidation of DsbB by quinones. In pathway B, the DsbA-DsbB complex is resolved by quinones without the interaction of the first periplasmic loop. Figure based on Fig. 8 in reference 84.
