Figure 6.
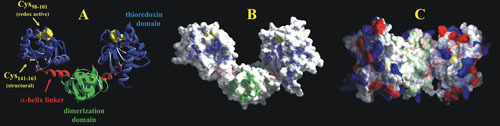
Domain organization of DsbC. (A) The crystal structure of the homodimer DsbC showing the two domains (thioredoxin in blue and dimerization in green) separated by the short α-helix linker in red (PDB accession number 1EEJ). Redox-active cysteines (C98 to C101) are represented as yellow spheres, and the structural disulfide bond (C141 to C163) is indicated. (B) The molecular surface of DsbC is superimposed, visualizing the pocket formed by the dimerization of DsbC. (C) Top-down view of DsbC displaying the noncharged pocket devoid of acidic (red) and basic (blue) amino acid residues.
