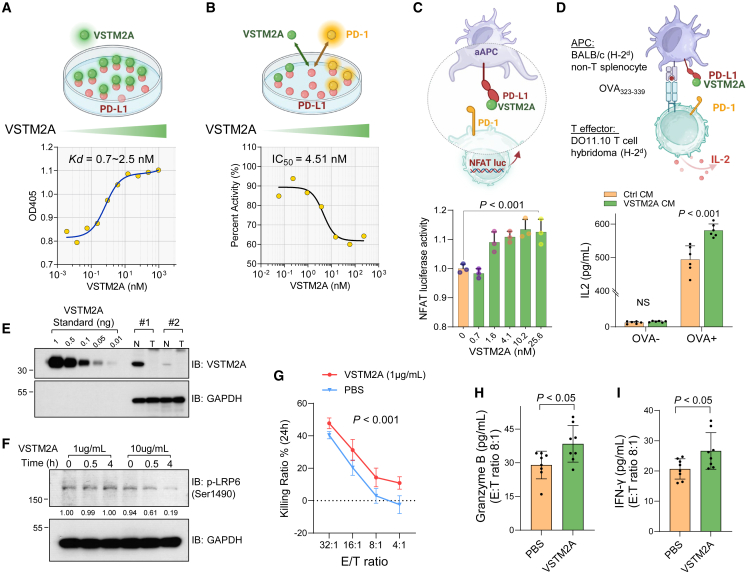
Figure 5.
VSTM2A attenuates PD-L1/PD-1 signaling and promotes T cell activity
(A) Determine the dissociation constant of human VSTM2A and PD-L1 using titration ELISA. (B) Determine VSTM2A IC50 using PD-L1/PD-1 inhibitor screening ELISA assay. (C) Recombinant VSTM2A protein induced NFAT-RE luciferase activity dose dependently in PD-1/PD-L1 blockade bioassay. (D) IL-2 production from DO11.10 T cells upon co-culture with APCs in the presence of VSTM2A conditioned medium or control medium. (E) VSTM2A protein level in human CRC and adjacent normal tissue was determined by western blot. 20 μg total protein was loaded per lane. Recombinant VSTM2A protein was as a standard curve (0.01–1 ng was loaded per lane). (F) Human T cells were stimulated with 1 or 10 μg/mL recombinant VSTM2A protein for 30 min and 4 h. Phosphorylation of LRP6 (Ser1490) was evaluated using western blot. (G) Killing assays showing the percentage of cytotoxicity of wild-type T cells against HCT116 (a PD-L1-positive CRC cell line) in the presence of 1 μg/mL VSTM2A or PBS for 24 h. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. The experiment was repeated three independent times. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used. (H) The secretion of granzyme B and (I) IFN-γ from the co-culture supernatant with HCT116 cells in the killing assay was determined using ELISA. APC, antigen-presenting cell; CM, conditioned medium; N, adjacent normal; T, tumor; E, effector; T, target cell.