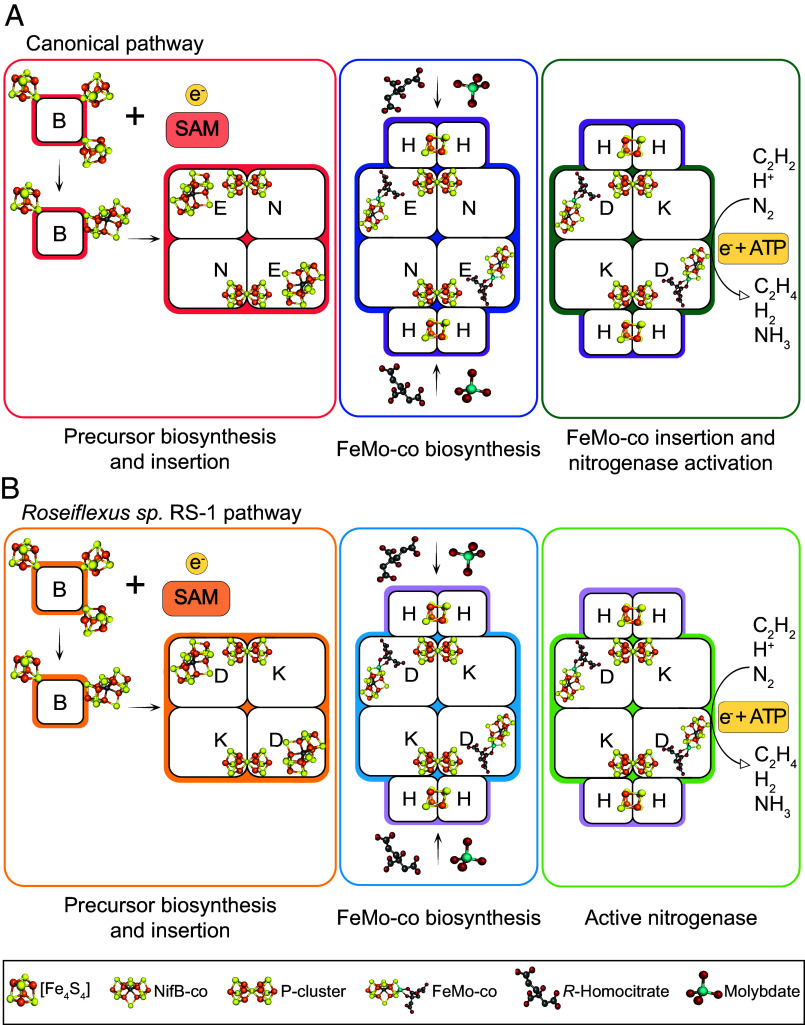
Fig. 1.
Schemes of FeMo-co biosynthetic pathways. (A) Canonical NifEN-dependent pathway as studied in Azotobacter vinelandii. The S-adenosylmethionine [SAM]-radical enzyme NifB synthesizes the [Fe8S9C] cluster NifB-co, which is then inserted into NifEN. FeMo-co biosynthesis occurs at the NifEN scaffold by substituting Mo for an apical Fe atom and adding R-homocitrate. FeMo-co biosynthesis requires the interaction of NifH with NifEN. FeMo-co is then transferred to apo-NifDK (already containing mature P-clusters) to reconstitute active NifDK. (B) Putative NifEN-independent pathway of Roseiflexus. The SAM-radical enzyme NifBRS synthesizes the [Fe8S9C] cluster NifB-co, which is then inserted into apo-NifDKRS (already containing mature P-clusters or its precursors). FeMo-co biosynthesis occurs in situ in apo-NifDKRS and requires the interaction with NifHRS. After FeMo-co biosynthesis, mature NifDKRS is formed.