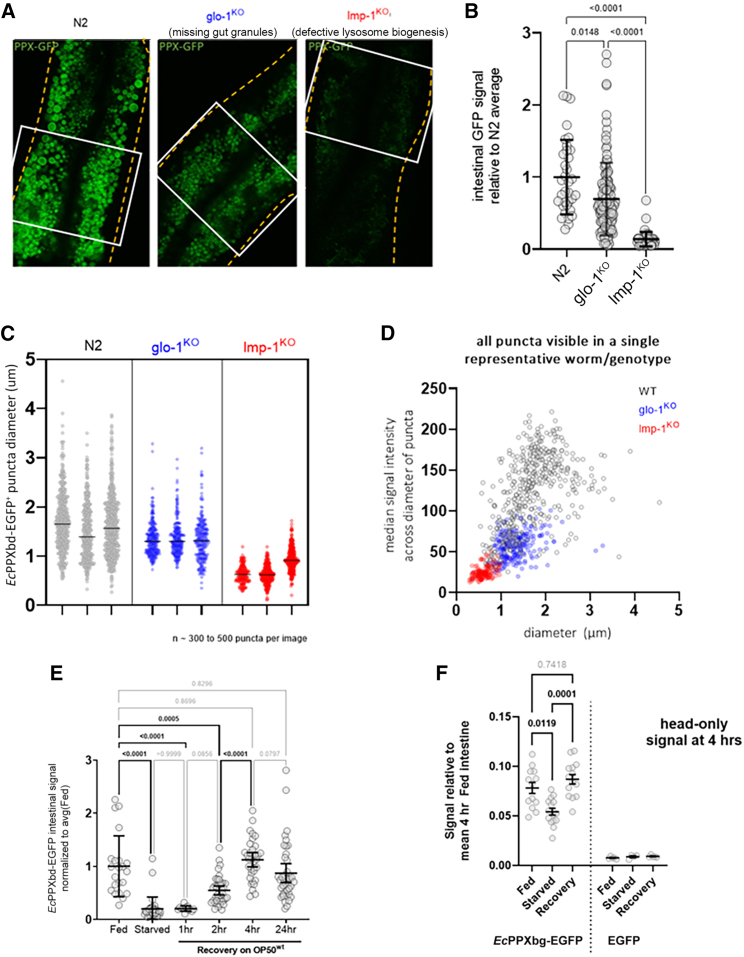
Figure 4.
Gut EcPPXbd-EGFP signal is dependent on endo-lysosomal vesicle formation and food availability
(A) Representative images of N2, glo-1KO, and lmp-1KO day 1 adults stained with EcPPXbd-EGFP. Cuticle of worm is denoted by a dashed yellow line. Area used for fluorescence measurement in Figure 3B is shown with a white rectangle. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
(B) Relative fluorescence of EcPPXbd-EGFP signal in intestine. Each circle is one worm. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post hoc was used. Error bars are mean +/− SD.
(C) Quantification of diameter of EcPPXbd-EGFP-positive puncta in three representative images from 3 separate worms of intestinal cells. Bar = median. Each dot is one punctum.
(D) Graph of signal intensity of each puncta by its diameter. Each circle is one punctum.
(E) Quantification of EcPPXbd-EGFP before and after food removal and recovery. Each dot represents one worm. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post hoc was used. p value is shown for each comparison made. Error bars are mean +/− SEM.
(F) Relative fluorescence of EcPPXbd-EGFP signal in the heads of worms relative to the fed 4 h intestinal signal. Each circle is one worm. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post hoc was used. Lines are mean ± SEM. p value is shown for each comparison made. All comparisons between GFP only groups had p > 0.4.