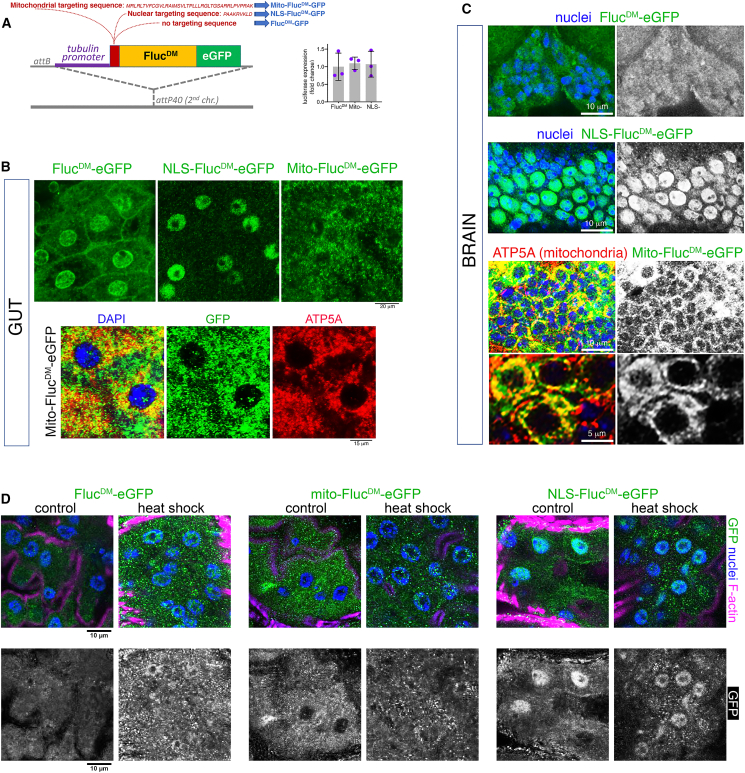
Figure 1.
Generation of compartment-targeted, misfolding-prone FlucDM variants to perturb and sense subcellular proteostasis in Drosophila
(A) Generation of transgenic organelle-targeted sensors of protein quality control based on a misfolding-prone mutant firefly luciferase (FlucDM) fused to EGFP. The mitochondrial targeting sequence from the human mitochondrial COX VIII protein was utilized to generate the mito-FlucDM variant, whereas a standard nuclear targeting sequence was used to generate the NLS-FlucDM. General (untargeted) sensors and reporters for mitochondria and the nucleus were site integrated and are expressed ubiquitously (downstream of a tubulin promoter) and at similar levels, as indicated by qRT-PCR with 3 batches of flies and the mean ± SD (no significant changes, one-way ANOVA).
(B) Immunostaining and confocal microscopy of enterocytes indicate that FlucDM variants exhibit the expected specificity in subcellular localization. General (untargeted) FlucDM is detected in the cytoplasm (but also in the nucleus and plasma membrane), mito-FlucDM is detected in ATP5A-stained mitochondria, and NLS-FlucDM is found in the nucleus. Scale bars represent 20 and 15 μm, as indicated.
(C) Immunostaining and confocal microscopy of brain cells from the antennal lobe indicates a similar localization. The untargeted FlucDM is detected in the cytoplasm, mito-FlucDM is detected in ATP5A-positive mitochondria, and NLS-FlucDM is found in the nucleus. Scale bars represent 10 and 5 μm.
(D) Immunostaining of enterocytes from heat-shocked and control flies identifies FlucDM-GFP aggregates that accumulate in the cytoplasm in response to thermal stress compared to non-heat-shocked controls. Similar heat-induced cytoplasmic aggregates are also found in heat-shocked NLS-FlucDM-EGFP and mito-FlucDM-EGFP cells. In the case of mito-FlucDM-EGFP, these aggregates are recognizable because they produce larger puncta than the staining that corresponds to mito-FlucDM-EGFP-positive mitochondria (B). Scale bar, 10 μm.