Figure 2.
Use of compartment-targeted FlucDM variants to perturb subcellular proteostasis
FlucDM are misfolding-prone proteins and, therefore, they may challenge proteostasis in the subcellular compartment to which they are targeted. On this basis, FlucDM variants can be used as tools to induce a moderate perturbation of subcellular proteostasis when compared to an isogenic control with no FlucDM expression.
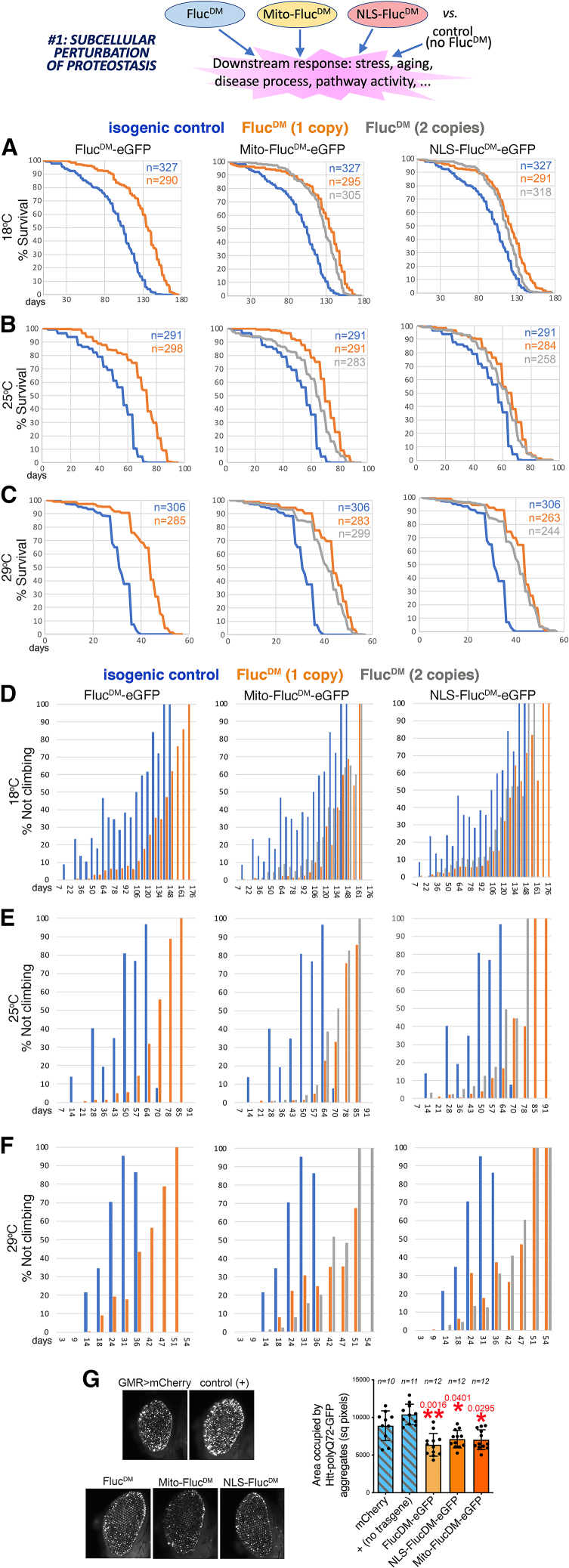
(A–C) The untargeted (cytoplasmic) FlucDM, the mitochondrially targeted mito-FlucDM, and the nucleus-targeted NLS-FlucDM extend lifespan (p < 0.001, log -rank test, with n indicated) when compared to isogenic controls with no FlucDM. Distinct FlucDM variants have effects of different magnitudes; the untargeted FlucDM is more effective in extending lifespan at 18°C (A) and at 25°C (B) compared to NLS-FlucDM, whereas similar lifespan extension is seen at 29°C (C) for all FlucDM variants. These findings suggest that moderate perturbation of subcellular proteostasis by FlucDM variants induces a stress response that extends lifespan. A single (orange) or 2 copies (gray) of the FlucDM transgenes similarly extend lifespan compared to the isogenic controls with no FlucDM (blue).
(D–F) Negative geotaxis assays indicate that expression of misfolding-prone FlucDM proteins targeted to distinct subcellular compartments reduces age-related neuromuscular dysfunction during aging compared to isogenic controls that do not express FlucDM. A similar protection is found at 18°C (D), 25°C (E), and 29°C (F). These findings suggest that moderate perturbation of subcellular proteostasis by compartment-targeted FlucDM variants induces an adaptive stress response that improves neuromuscular function; p < 0.001 (log -rank test) with n indicated (A–C).
(G) Aggregates of GFP-tagged pathogenic huntingtin-polyQ can be seen in the retina of GMR>Htt-polyQ72-GFP flies at 30 days of age, but the total area of such aggregates is higher in controls (mCherry and no transgene, +) compared to flies that express FlucDM variants. This suggests that moderate stress induced by FlucDM can induce a hormetic stress response that improves proteostasis. The n (biological replicates) and the mean ± SD are indicated, with ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA).