Fig. 4. Zebrafish abcb6 knockdown affects lateral line development in zebrafish.
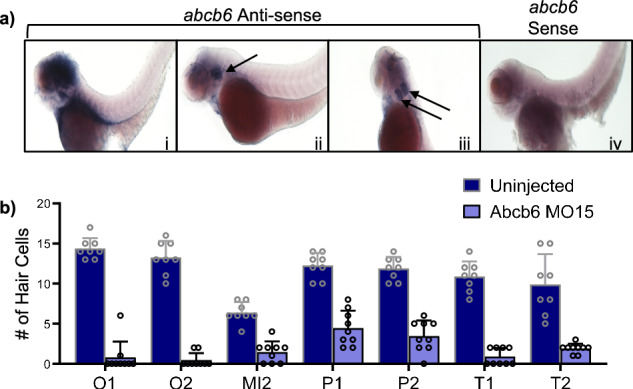
a Whole mount in situ hybridization (WISH) of 3 dpf AB zebrafish shows Abcb6 expression in the inner ear when treated with a zebrafish abcb6 anti-sense mRNA probe (i-iii). The auditory vesicle is denoted with black arrows. Zebrafish Abcb6 expression is not detected with a zebrafish abcb6 sense mRNA probe (iv). b Zebrafish Abcb6 MO15 morphants (purple) developed a reduced number of hair cells compared to WT (indigo) in zebrafish neuromasts. Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA with genotype and neuromast as factors. There is a significant main effect of genotype (F1,111 = 126.6, p < 0.0001) and neuromast (F6,111 = 6.13, p < 0.0001). O1, O2, and MI2 neuromasts are found on the head, P1 and P2 represent the first two neuromasts of the posterior lateral line (trunk), and T1 and T2 are the two terminal-most neuromasts on the tail (neuromast nomenclature modified from Raible and Kruse, 2000)90. Hair cell counts are from 3 dpf brn3c transgenic larvae, N = 8 fish for uninjected, N = 9 fish for Abcb6 MO15, bars represent mean + 1 SEM. The person counting hair cells was blinded to treatment. Experiment was repeated and the results showed the same pattern. Source data from (b) are provided in the Source Data file.
