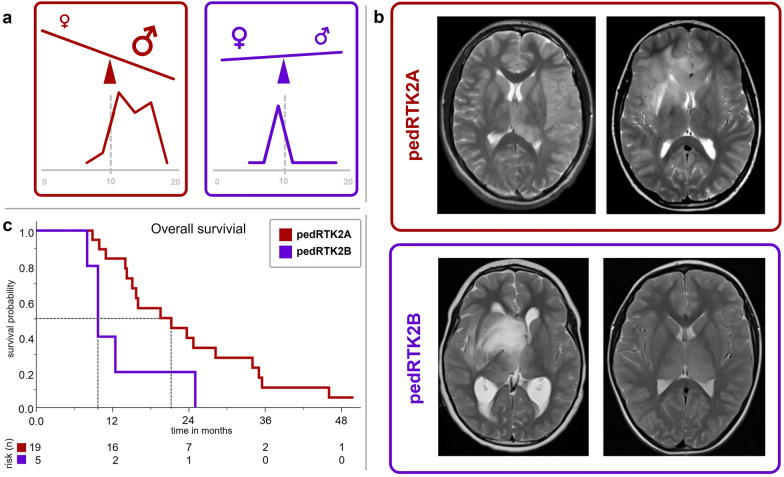
Fig. 2.
Comparison of main clinical parameters in pedHGG-RTK2A/B (pedHGG-RTK2A = red; pedHGG-RTK2B = purple) a Sex distribution and age according to subclass. Children with pedHGG-RTK2B were significantly younger (Graphic in the bottom row each ranging from 0 to 20 years of age; p = 0.01). b T2-weighted axial MR images of patients with pedHGG-RTK2A and pedHGG-RTK2B tumors, respectively. pedHGG-RTK2A (left); a diffuse infiltrating glioma mainly affecting the left parietal lobe at diagnosis is shown. This patient developed a gliomatosis cerebri (GC) phenotype (secondary GC) at progression; (right): a case with GC phenotype at diagnosis (primary GC). pedHGG-RTK2B (left); a glioma with diffuse infiltration of the midline (mesencephalon, basal ganglia and opticohypothalamic region) reaching the right temporal lobe. (right): a bithalamic tumor. c Kaplan–Meier plot displaying the overall survival (50% survival probability marked) of the two methylation-based subclasses