Figure 5.
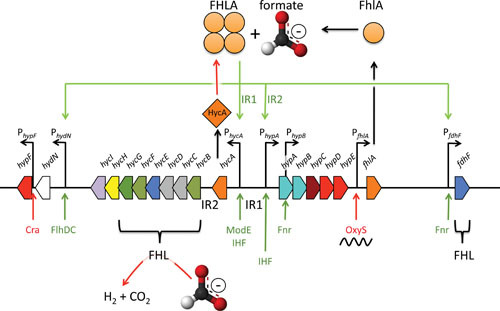
Organization of the FHLA-dependent formate regulon. The genes and distances are not to scale; the color scheme of genes is according to Fig. 3. The fhlA gene product oligomerizes as a homotetramer and is able to sense formate under fermentative growth conditions, whereupon it activates transcription (green arrows). The binding site for hyc activation is intergenic region 1 (IR1) and for hyp is IR2. FHLA autoactivates its own transcription via the hyp promoter; in the absence of formate, it is transcribed at a low constitutive level from its own promoter. The function of FHLA is antagonized by HycA, and by the small RNA OxyS, which binds to its mRNA, and the FHL complex removes the activating molecule formate (red arrows). Further transcriptional regulators to the respective promoters are shown in red (inhibiting) or green (activating).
