Figure 1.
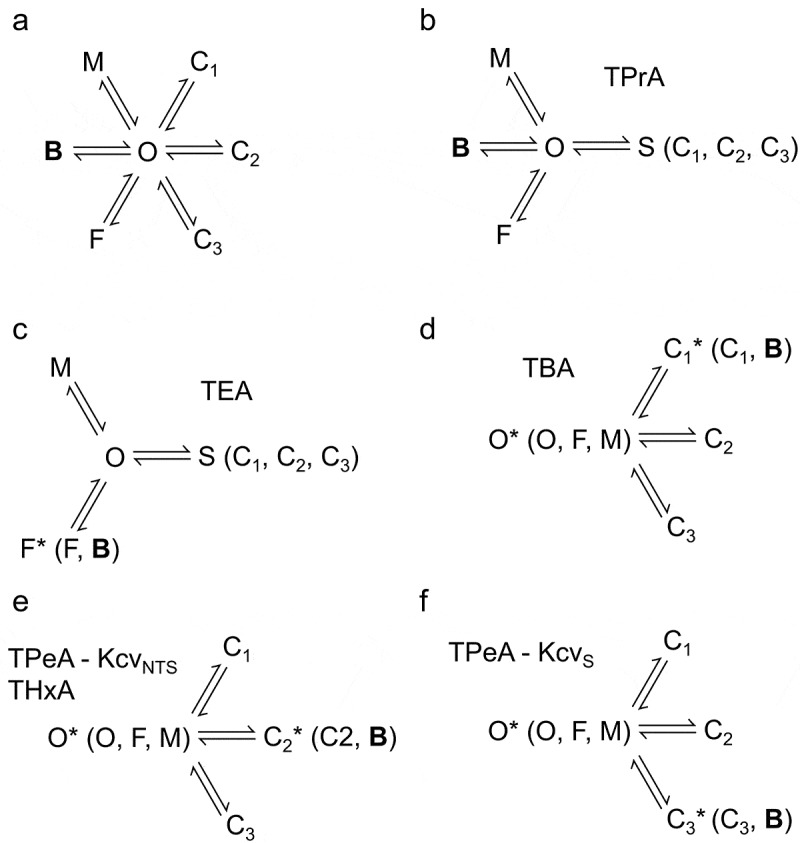
Markov models used for the fitting of the blocking kinetics. (a) The full Markov model with all states as known so far from previous studies [2,3,29] supplemented by the blocked state B. The states C1, C2 and C3 belong to slow gating with dwell times longer than a millisecond, with C3 occurring only in KcvS due to its cytosolic gate [2]. These states can be analyzed by a jump detector and dwell time analysis. F and M belong to fast gating (dwell-time in F about 5 µs) and medium gating (dwell-time in M is voltage-dependent ranging between 150 µs to 40 µs) [3]. (b, c) The models used for the analysis of fast blockers. C1 - C3 cannot be resolved by the beta distribution analysis and are merged into S (“slow”). (c) For TEA, B has a similar dwell time as F, so the two states cannot be kinetically separated. (b) for TPrA, this separation is possible [7]. (d,e,f) in the experiments with slow blockers, the dwell time in B coincides with one of the slow states C1 - C3. Thus, only two (KcvNTS) or three (KcvS) closed states are detected in the dwell time histograms. The inclusion of B is identified by concentration dependence. O,F,M are merged into an apparent open state O*. Definition: The rate constant of the transition from a state X to a state Y is called kXY. kBO as the rate constant of blocker dissociation is also called koff.
