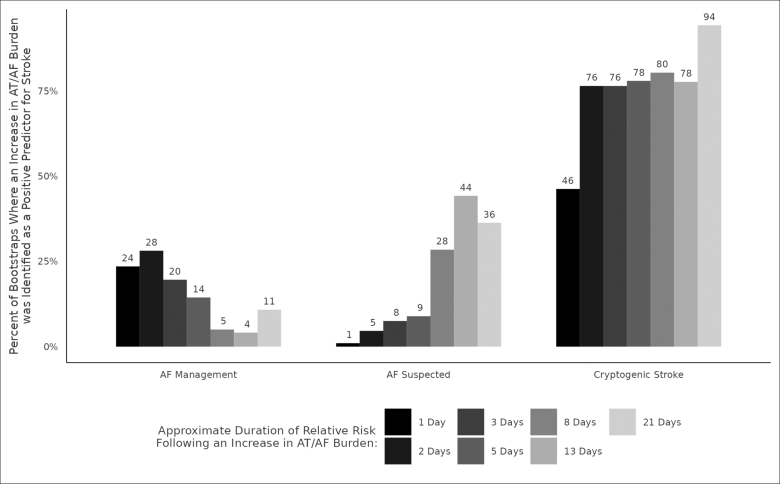
Figure 4.
Temporal association of atrial tachycardia (AT)/atrial fibrillation (AF) burden trend and stroke risk. The temporal relationship between AT/AF burden and ischemic stroke risk differed by device indication with AF management prioritizing shorter durations of risk (1–5 days) more frequently than longer durations and cryptogenic stroke selecting a longer duration of risk (21 days) more frequently than shorter durations. While a 21-day simple moving average, offset with its cumulative moving average was the most robust temporal trend across device indications (Figure 3, inset), its frequency of selection as a predictor differed by indication, occurring 94% of the time for cryptogenic stroke and 11% of the time for AF management.