Figure 4.
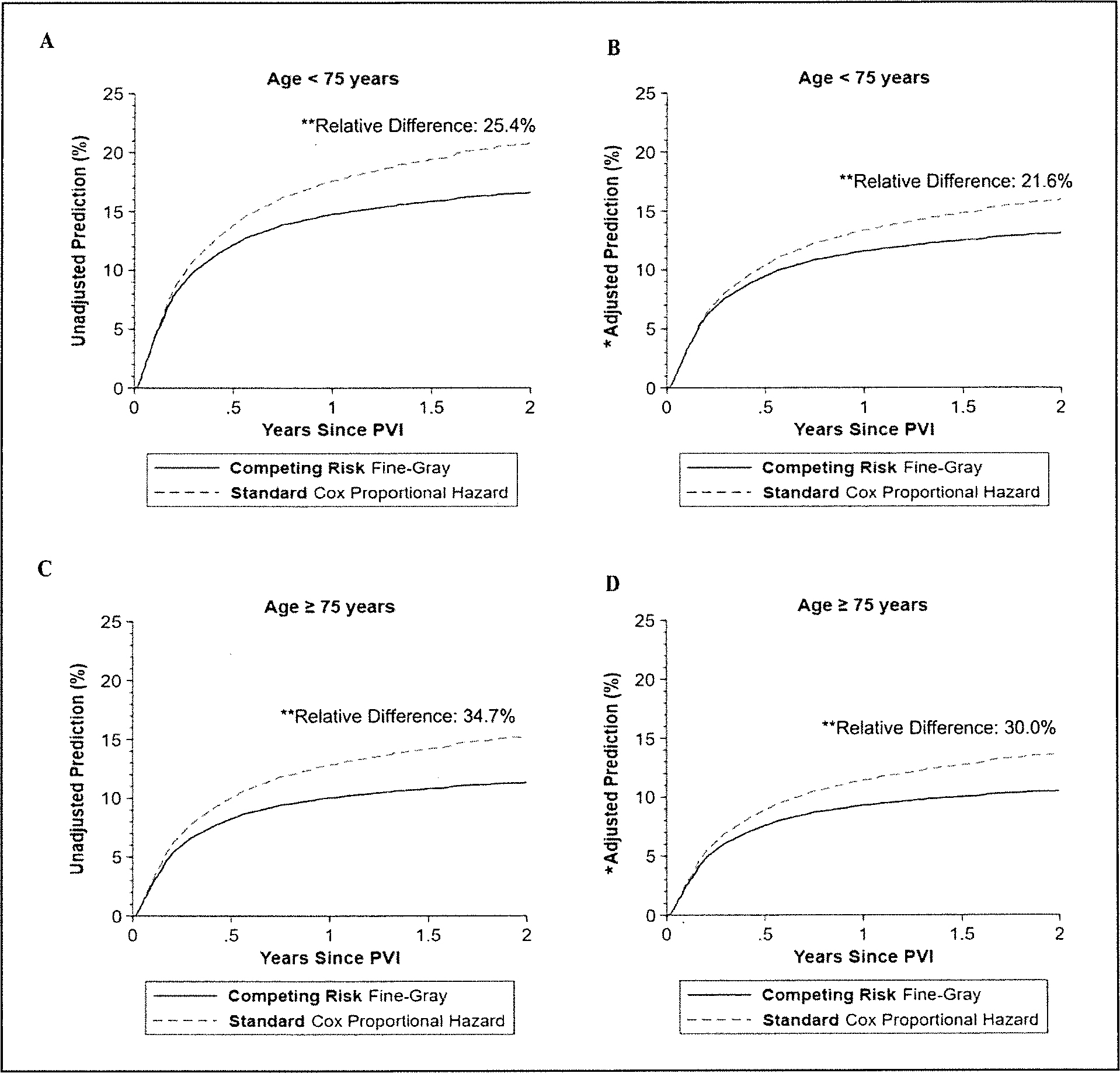
The unadjusted and adjusted prediction of the 2-year risk of major amputation in patients aged < 75 years (A and B) versus those aged ≥ 75 years (C and D) from the standard time-to-event Cox proportional hazards regression model and from the competing risk Fine–Gray regression model in the CLTI cohort.
*Regression model adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity. site, insurance, living at home, smoking guideline-directed medical therapy, hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, percutaneous intervention, coronary artery bypass grafting, diabetes. chronic kidney disease, endarterectomy or carotid stenting, major or minor amputation, bypass, endarterectomy or peripheral vascular intervention. and urgency of the procedure.
**All relative differences were calculated before rounding the estimators.
CLTI, chronic limb-threatening ischemia; PVI, peripheral vascular intervention.
