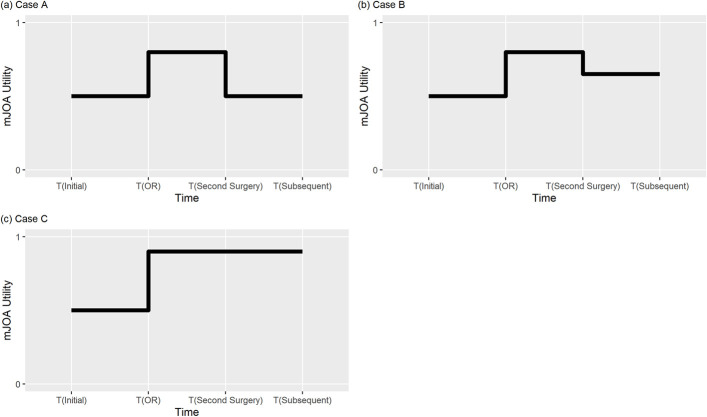
Fig. 1.
Modeling of quality of life for surgically treated patients. In all cases, surgical patients immediately experienced a neurologic improvement in the mJOA score after the first surgery (OR). The magnitude of change was drawn from a probability distribution for change scores obtained from the pooled published data (Appendix 2). In Case A, at the time to second surgery (TTSS), patients reverted to their baseline mJOA health state; for example, this corresponds to patients with adjacent-segment disease developing worsening myelopathy without neurologic improvement following the second surgery. In Case B, at TTSS, patients were assigned a utility between the baseline mJOA health state and neurologically improved mJOA health state; for example, this corresponds to patients with adjacent-segment disease developing worsening myelopathy, with neurologic improvement following the second surgery. In Case C, at TTSS, patients did not experience a decline in mJOA health state; for example, this corresponds to patients undergoing a second surgery for pseudarthrosis.