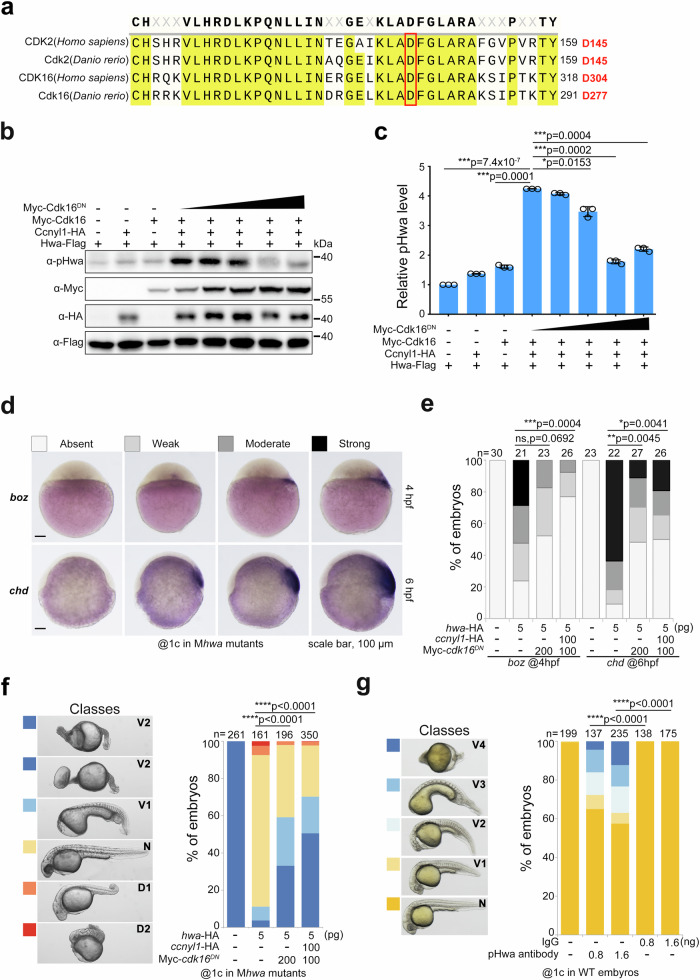
Fig. 6. Attenuating phosphorylation of Ser168 by Cdk16DN or pHwa antibody disrupts the axis-inducing activity of Hwa.
a Residue conservation analysis of human CDK2/16 and zebrafish Cdk2/16 proteins. The red box indicates the conserved, functionally critical aspartic acid (D). b Immunoblotting of pHwa in HEK293T cells transfected with Hwa-Falg, wild-type Cdk16, and different doses of dominant negative Cdk6 (Myc-Cdk16DN). c Quantifications of relative pHwa levels in HEK293T cells treated as in (b), N = 3.Total Hwa protein was used as an internal control. d The WISH results of boz and chd in cdk16DN mRNA injected embryos at 4 hpf and 6 hpf, respectively. e The statistical results of embryos treated as in (d). f Effect of coexpression of cdk16DN and ccnyl1-HA mRNA with hwa mRNA in Mhwatsu01sm embryos, N = 3. g Phenotypes of wild-type embryos injected with pHwa antibody or IgG at different doses, N = 4. Scale bars, 100 μm; V, ventralized; N, normal; D, dorsalized. Total Hwa proteins were used as references for quantification in (c). c A two-tailed unpaired t-test was performed and data were presented as mean ± SD. e–g A two-tailed Fisher’s exact test was performed to evaluate differences between treatments (all phenotypes were divided into two groups: Unchanged and Changed). N, number of biological replicates; n, total number of embryos in each treatment; Significant differences are indicated by ns ≥ 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.