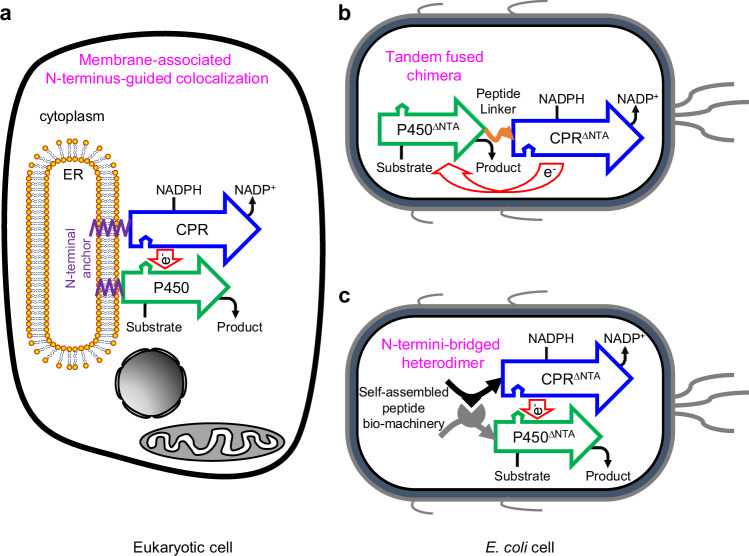
Fig. 1. Employing self-assembled peptide bio-machinery for spatial organization of eukaryotic P450 system.
a Eukaryotic P450 enzymes belong to Class II P450 system, in which P450 enzymes and their redox partner NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR) generally colocalize on the cytoplasmic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane through a short hydrophobic N-terminal anchor (NTA). b In E. coli, soluble cytoplasmic regions of eukaryotic P450 system are manipulated to form a functional chimera, using a flexible peptide linker indicated by the orange curve with a single arrow. c Self-assembled peptide bio-machinery, in this study, was harnessed to modularly reconstruct eukaryotic P450 system and finely tune the protein architecture in E. coli. The N-termini-bridged heterodimer was achieved via self-assembling the N-terminus-reconstructed P450 and CPR as a mimic counterpart of eukaryotic P450 system. The hollow arrow represents a polypeptide from the N-terminus to the C-terminus. The superscript ∆NTA indicates that the N-terminal anchor of the protein was truncated.