FIGURE 3.
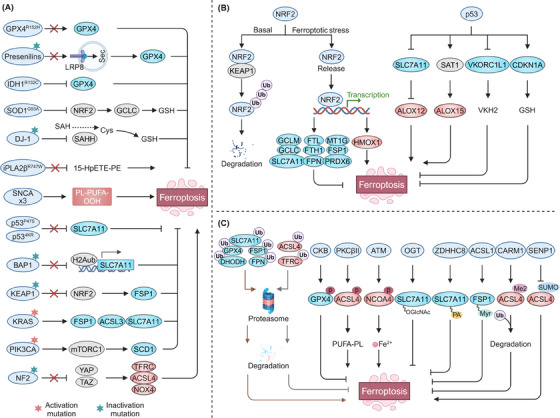
Nonepigenetic regulation in ferroptosis. (A) Genetic mutations in neurodegenerative diseases and cancers are key modulators of pathways influencing ferroptosis susceptibility as shown. (B) NRF2 transcriptionally regulates genes involved in GSH and GPX4 biosynthesis, iron metabolism, NADPH production, and FSP1, thereby modulating cellular susceptibility to ferroptosis. TP53 transcriptionally inhibits SLC7A11 and VKORC1L1 and upregulates SAT1, sensitizing cells to ferroptosis. However, under cystine deprivation, TP53 suppresses ferroptosis by promoting CDKN1A expression. (C) Core ferroptosis‐regulating proteins, including SLC7A11, GPX4, ACSL4, FSP1, and DHODH, can undergo multiple PTMs, such as ubiquitination, phosphorylation, acetylation, O‐GlcNAcylation, S‐palmitoylation, N‐myristoylation, methylation, and SUMOylation, thereby influencing ferroptosis sensitivity. ACSL4, acyl‐CoA synthetase long‐chain family member 4; ALOX, arachidonate lipoxygenase; BAP1, BRCA1‐associated deubiquitinase 1; CARM1, coactivator‐associated arginine methyltransferase 1; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FPN, ferroportin; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; FTH1, ferritin heavy chain 1; GCH1, GTP cyclohydrolase‐1; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; HMOX1, heme oxygenase 1; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; iPLA2β, phospholipase A2β; KEAP1, kelch‐like ECH‐associated protein 1; NF2, neurofibromin 2; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2‐related factor 2; OGT, O‐linked N‐acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) transferase; SAHH, s‐adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; SAT1, spermidine/spermine N1‐acetyltransferase 1; SCD1, stearoyl‐CoA desaturase; SENP1, SUMO‐specific peptidase 1; SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1; TF, transferrin; TFRC, transferrin receptor; VKORC1L1, vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1‐like 1. GCLC, glutamate–cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; SNCA, synuclein α; PIK3CA, phosphatidylinositol‐4,5‐bisphosphate 3‐kinase catalytic subunit α; YAP, Yes1‐associated transcriptional regulator; TAZ, transcriptional coactivator with PDZ‐binding motif; NOX4, NADPH oxidase 4; CDKN1A, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; CKB, creatine kinase B; ATM, ATM serine/threonine kinase; ZDHHC8, zinc finger DHHC‐type containing 8.
