FIGURE 4.
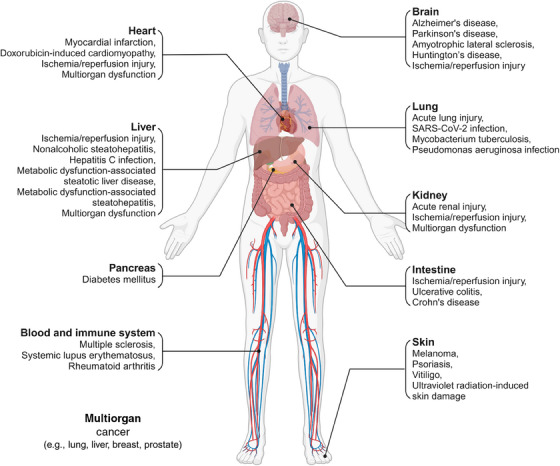
Role of ferroptosis in various diseases across different organs and tissues. Ferroptosis serves as an intrinsic tumor‐suppressive mechanism, with its evasion supporting tumorigenesis and progression. Additionally, ferroptosis activation is implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple neurodegenerative diseases, organ injuries, metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease, and dermatological conditions such as psoriasis, vitiligo, and UV‐induced skin damage. Notably, due to its complex interaction with the immune system, ferroptosis may exert dual effects, particularly in immune and infectious diseases.
