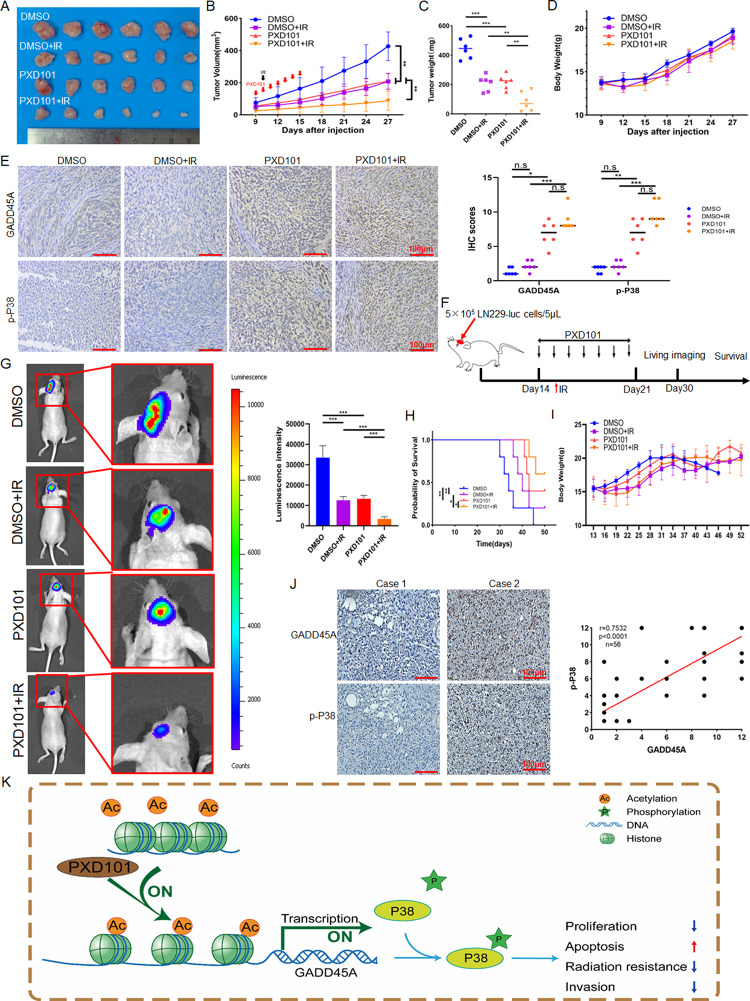
Fig. 6.
PXD101 inhibits the growth and radioresistance of GBM in vivo. A total of 1 × 107 LN229 cells were inoculated into the armpits of nude mice, and the PXD101 treatment group was injected intraperitoneally with PXD101 (50 mg/kg) for 7 days; the IR group was irradiated with 6 Gy after the first injection. (A-D): Tumor size (A), tumor volume (B), tumor weight (C), and body weight (D) were measured. (E) The representative images of IHC staining of GADD45A and p-P38 in xenograft tumor tissues (left). The statistical analysis of IHC score (right). (F) Schematic diagram of the orthotopic tumor mouse model. (G) Representative bioluminescence images of PXD101 or/and IR treatment after intracranial injection of LN229-luc cells in mice (n = 5) (left); quantitative analysis of the bioluminescence intensity (right). (H) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice. (I) The curves of mice body weight. (J) The representative images of IHC staining of GADD45A and p-P38 protein levels in clinical samples (left); the correlation analysis of GADD45A and p-P38 expression based on IHC score (right). (K) Schematic diagram of PXD101 inhibiting malignant progression and radioresistance of GBM by promoting GADD45A/p-P38 pathway. Scale bar, 100 μm. *P < 0.5, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001