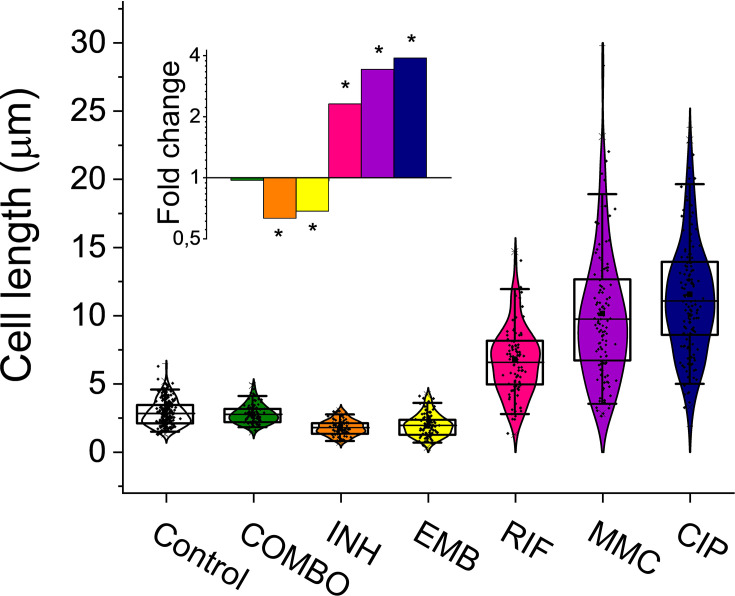
Figure 1. Cell length distribution of M.smegmatis cells treated with different drugs.
Horizontal lines represent the mean of the plotted data points (n=84–212). The inset shows the fold changes in cell length compared to the untreated control on a log2 axis, highlighting the phenotypic effect of each treatment. * indicates data significantly different from the control at p=0.0001. Numerical values and additional statistical parameters are provided in Figure 1—source data 1.