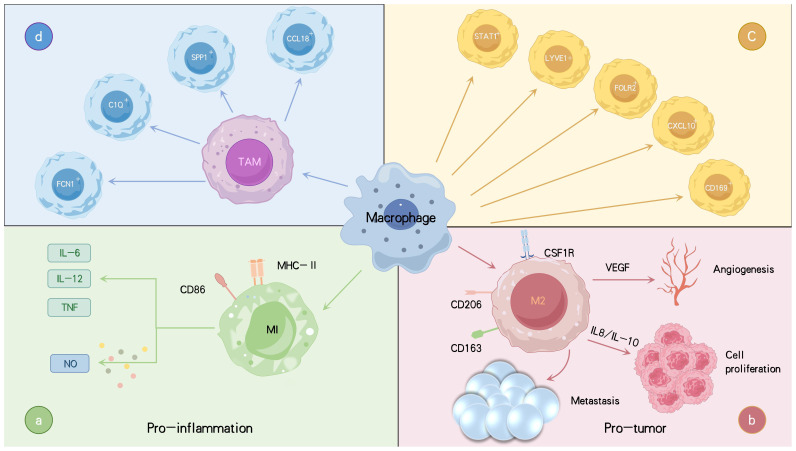
Figure 1.
Varieties of macrophages linked to tumors along with their primary functions and roles. TAMs are categorized into two main phenotypes: the anti-tumor M1 type, which secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α, produces NO, and promotes inflammation (A). The M2 type is pro-tumorigenic, secreting IL-8 and IL-10, which promote tumor progression and dissemination, as well as VEGF, which facilitates angiogenesis, thereby acting as a tumor promoter (B). Macrophages are further classified into subsets CD169+, STAT1+, LYVE1+, FOLR2+ macrophages (C). Recently, new TAM subtypes have been identified, including FCN1+, SPP1+, C1Q+, and CCL18+ TAMs, each with distinct functions in tumor progression and immune regulation (D). Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukins (IL), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), nitric oxide (NO).