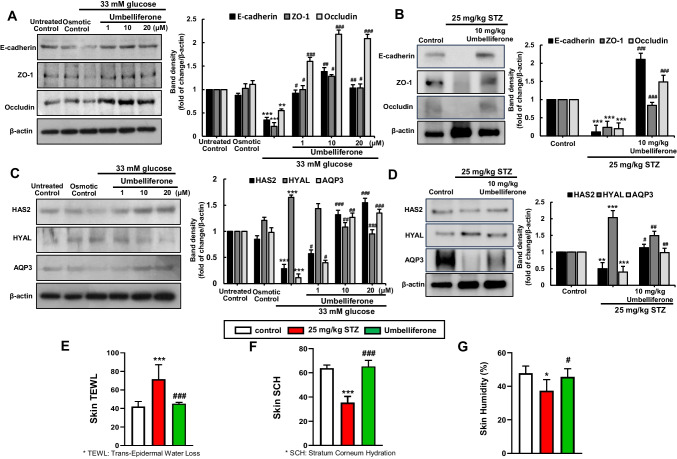
Fig. 6.
Western blot analysis of E-cadherin, ZO-, and Occludin in fibroblasts (A) and diabetic skin tissue (B). Alterations in the expression of proteins associated with skin tissue’s moisture retention ability, namely, HAS2, HYAL, and AQP3, were examined through western blot analysis in both fibroblast cells (C) and skin tissue (D). The right bar graphs represent the quantitative results of blots in A–D. Dermal fibroblast cells were cultured in a high-glucose medium for 3 days and treated with umbelliferone at concentrations ranging from 1 to 20 µM. The animal model involved intraperitoneal streptozotocin injections for 5 days, followed by oral administration of umbelliferone for 4 weeks. The indices measured included TEWL (trans-epidermal water loss), a metric quantifying moisture evaporation through the skin (E); skin SCH (stratum corneum hydration), a measure of moisture content in the skin’s outermost layer (F); and humidity, an indicator of overall skin moisture state (G). Measurements were conducted on the dorsal area of the mice (E–G). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for comparisons between the 33 mM glucose/diabetic mice and control groups/control mice; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 for comparisons between the 33 mM glucose/diabetic mice and umbelliferone-treated groups. Statistical significance of the mean values for each group was determined using ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. Data are expressed as means ± SD