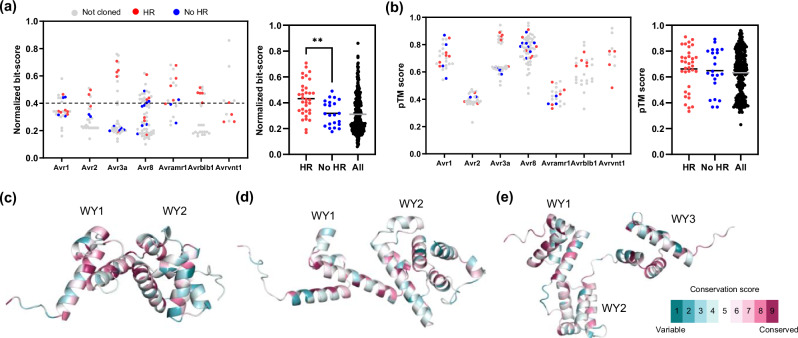
Fig. 4. Sequence and structure-based identification of homologous effectors enable to search broadly conserved effector families across the Phytophthora species.
a Normalized bit-score of 316 homologous effectors (of P. infestans, P. parasitica, P. cactorum, P. palmivora, and P. sojae) against corresponding reference P. infestans effectors are plotted (left). Red dots, blue dots, and gray dots represent HR positive, negative, and not cloned effectors, respectively. Average normalized bit-score of HR positive, negative, and 316 homologous effectors presented as black and gray bar (right). Average normalized bit-score of HR positive effectors (n = 34) was significantly higher than HR negative effectors (n = 22). Statistically significance is analyzed with unpaired t-test (two-tailed **P < 0.01). b pTM score of 316 homologous effectors against corresponding reference P. infestans effectors are plotted (left). Average pTM score of HR positive, negative, and 316 homologous effectors presented as black and gray bar (right). Average pTM score of HR positive effectors was not significantly different from HR negative effectors. Statistically significance is analyzed with unpaired t-test. c–e Predicted effector domain structures of PiAvr1 (c), PiAvr8 (d), and PiAvramr1 (e). The WY domain is represented by four α-helix units. The amino acid conservation scores of structures were calculated in ConSurf server using sequence alignment of HR-positive effectors.