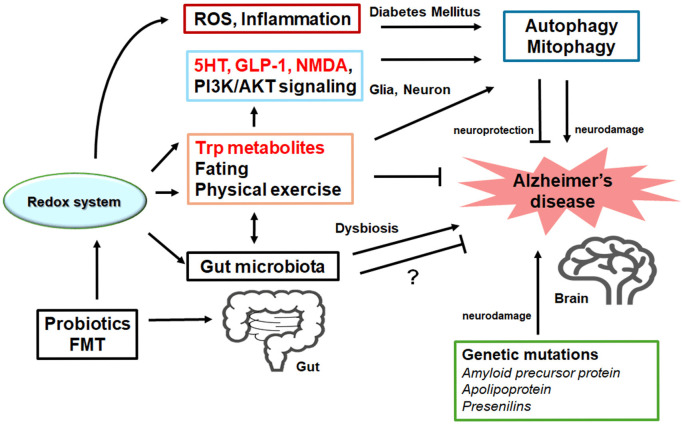
Figure 3.
Possible tactics for the neuroprotection and/or against the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease have been shown. One ideal approach might be to utilize agonists of serotonin (5HT) and GLP-1 receptors and/or antagonists of NMDA receptors with the use of tryptophan (Trp) metabolites to pause the neuron-damaging process for the neuroprotection. Probiotics and/or fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) might contribute to the alteration of gut microbiota, which could also be advantageous for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Note that several important activities such as inflammatory reaction, autophagy initiation/regulation, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production have been omitted for clarity. Stimulatory effects are indicated with arrows; inhibitory effects with a line ending with hammerhead. “?” means for author speculation.