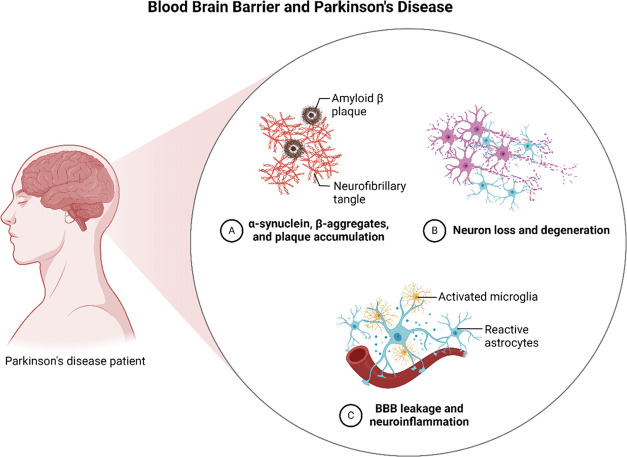
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and its function in Parkinson’s disease. The diagram illustrates the BBB (A) and its impairment in Parkinson’s disease (B), resulting in the buildup of harmful proteins such as amyloid-β plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, α-synuclein, and β-aggregates. Neuroinflammation is worsened by the presence of activated microglia and reactive astrocytes, leading to the loss and degeneration of neurons. The graphic emphasizes the crucial function of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) in obstructing the entry of hazardous compounds into the brain and the severe repercussions that occur when the BBB becomes permeable in Parkinson’s disease.