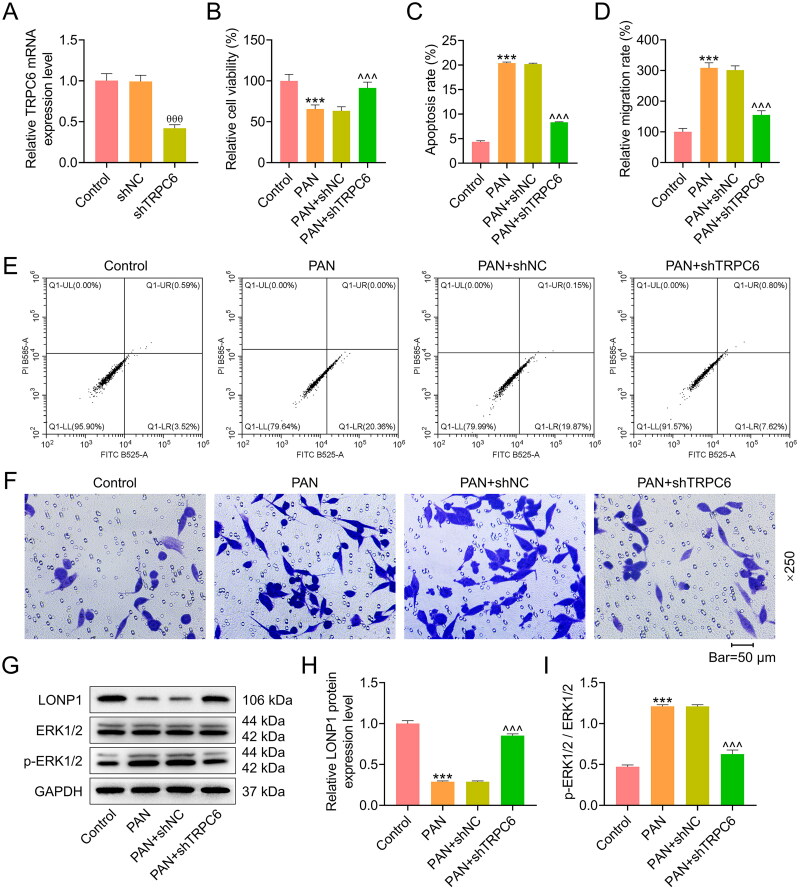
Figure 2.
Effects of TRPC6 silencing on viability, apoptosis, migration, ERK phosphorylation and LONP1 expression in PAN-treated podocytes.
AB8/13 cells were transfected with shTRPC6 or shNC, and then treated with 30 µg/ml PAN for 48 h. (A) The efficiency of TRPC6 knockdown was determined by qRT-PCR. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene control. (B) The viability of AB8/13 cells in the Control, PAN, PAN+shNC, and PAN+shTRPC6 groups was assessed by cell counting kit-8 assay. (C, E) The apoptosis rate of AB8/13 cells in each group was detected by flow cytometry. (D, F) The percentage of migrating cells in each group was determined by transwell assay (magnification: ×250, scale bar = 50 µm). (G-I) The protein expression level of LONP1 and the ratio of p-ERK1/2/ERK1/2 were measured by Western blot. GAPDH was taken as the loading control. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; ***p < 0.001 vs. Control; θθθp < 0.001 vs. shNC; ^^^p < 0.001 vs. PAN+shNC. Abbreviation: TRPC6, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 6; shTRPC6, short hairpin RNA targeting TRPC6; shNC, shRNA negative control; PAN, puromycin aminonucleoside; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LONP1, Lon peptidase 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p-ERK, phosphorylated ERK.