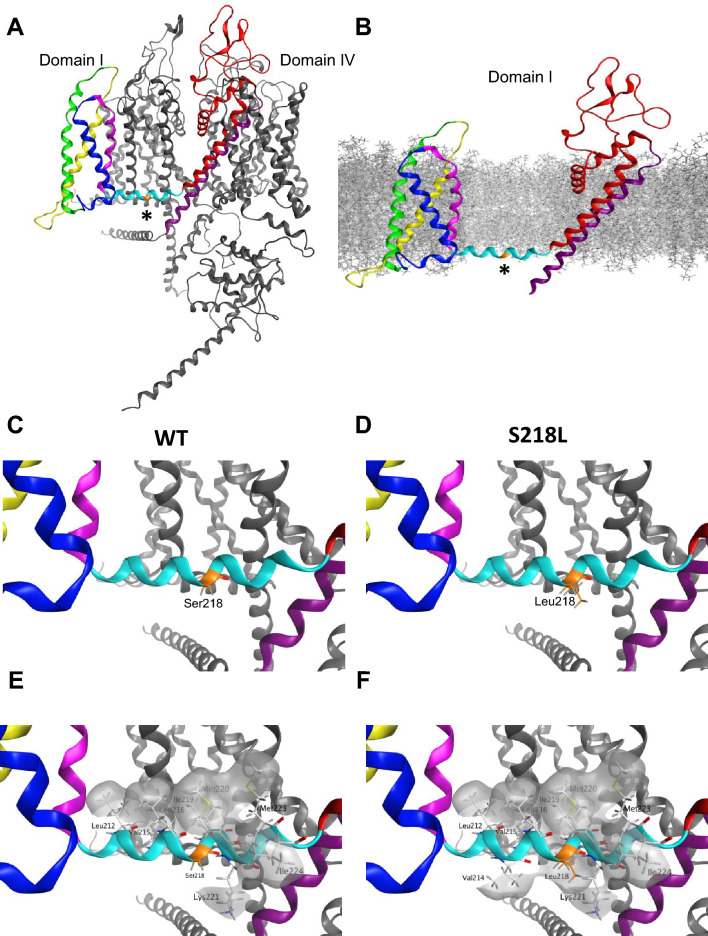
Fig. 4.
Molecular modeling of Cav2.1 S218L mutation depicts increased hydrophobicity in domain I S4-S5 linker. A Membrane view of Cav2.1 cryo-EM structure. VSD I is highlighted with S1 in yellow, S2 green, S3 blue and S4 pink, S4-S5 linker cyan, S5 red and S6 in purple. The location of Ser218 residue (*) is shown in orange. B Location of the Ser218 residue (*) with respect to modeled membrane in the isolated domain I. In a depolarized state, S4-S5 linker runs parallel to the inner surface the membrane. C–D) Orientation of WT Ser218 and Leu218 residues. Both Ser218 and Leu218 do not interact with any residues in neighboring domains. E The hydrophobic residues of the amphipathic domain I S4-S5 linker in WT are aligned on one side of the alpha helix, forming a hydrophobic patch (grey). F S218L mutation introduces a hydrophobic amino acid on the surface of the alpha helix facing the cytoplasm, increasing hydrophobicity with Val214 and Leu218