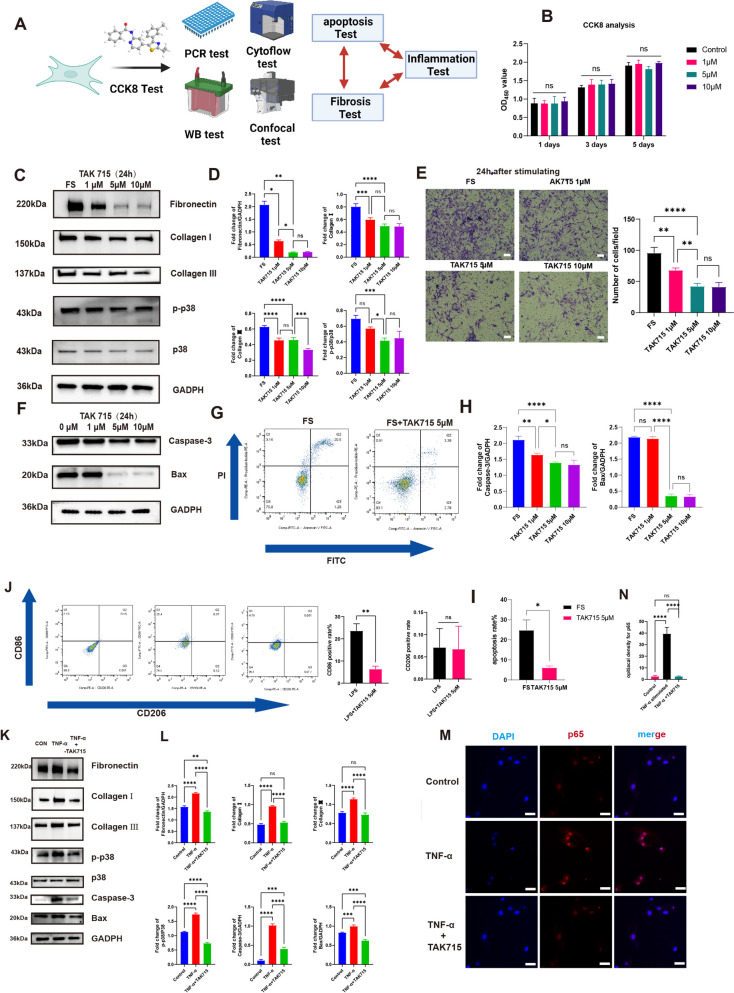
Fig. 4.
The TAK715 was safe and could reverse the fibrotic process of FS synovium fibroblasts and the inappropriate SFs apoptosis was inhibited during this process. Moreover, the TAK715 showed remarkable anti-inflammatory effects. A The flowchart of the fibrosis and inflammation experiments. B The CCK 8 analysis confirmed the TAK715 was safe for synovium fibroblasts at the concentration of 1 μM, 5 μM and 10 μM. C, D The western blot analysis of the TAK715 effect on reversing the fibrotic process of FS synovium fibroblasts. The statistic results (n = 3) confirmed that the TAK715 could reverse the fibrotic process of FS synovium fibroblasts at the final concentration of 1 μM, 5 μM and 10 μM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001. E The transwell analysis confirmed the TAK715 could decrease the migration ability of FS synovium fibroblasts, which was consistent with the western-blot analysis. Scale bar: 1000 μM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001. F, G, H, I the TAK715 could inhibit the FS synovium fibroblasts apoptosis at the effective concentration of 5 μM and 10 μM in western-blot (F)(H) and flow cytometry analysis(G)(I). J the flow cytometry of the TAK715 effect on inhibit the M1 polarization. K, L The western blot analysis of the TNF-α stimulating the control synovium fibroblasts into the fibrotic process and the TAK715 could inhibit this stimulation on synovium fibroblasts. The statistic results (n = 3) confirmed that the TNF-α could stimulate the control synovium fibroblasts into the fibrotic process at the final concentration of 100 ng/mL significantly and the TAK715 could inhibit this process at 5 μM effectively. M, N the confocal image showed that under the stimulation of TNF-α at 100 ng/mL the p65 enter the cell nuclear to perform the subsequent process and the TAK715 could interpose this process at 5 μM. Scale Bar: 50 μm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001